Portfolio/Evaluation
210 likes | 533 Vues
Portfolio/Evaluation. Sinn und Zweck eines Portfolios. Gegenstand: gegliederte Sammelmappe von Dokumenten zur Vorlage Sinn: – Bewusstwerden von eigenen Lernfortschritten (selbstgesteuertes Lernen) – Reflexion über Lernen und Leisten, – Leistungsdokumentation und Leistungs bewertung.

Portfolio/Evaluation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sinn und Zweck eines Portfolios Gegenstand: gegliederte Sammelmappe von Dokumenten zur Vorlage Sinn: – Bewusstwerden von eigenen Lernfortschritten (selbstgesteuertes Lernen) – Reflexion über Lernen und Leisten, – Leistungsdokumentation und Leistungs bewertung
Europäisches Sprachenportfolio Ziel: Transparenz und Vergleichbarkeit bezogen auf sprachliche Kenntnisse und Fertigkeiten innerhalb der Europäischen Union
Bestandteile des ESP Sprachenpass: Dokumentation sprachlicher Kompetenzen; sechs Stufen als europaweiter Referenzrahmen
Bestandteile des ESP Sprachenbiografie: individuelle Einschätzung ihrer Fähigkeiten und interkulturellen Erfahrungen durch die Lernenden selbst
Bestandteile des ESP Dossier: Beispiele persönlicher Leistungen, z.B. besonders gelungene Arbeiten, Texte, Video-/ Audio-Kassette etc
Pädagogische Funktion des ESP Pädagogische Funktionen: • Lernende verfolgen ihre eigenen Lernprozesse, • Portfolio schafft Anreize, lebensbegleitend Sprachen zu lernen, • Portfolio stärkt Selbstständigkeit und Selbstverantwortung der Lernende
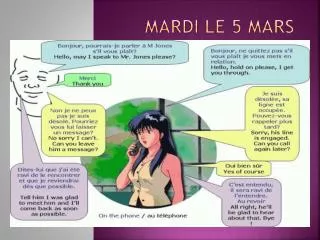
Beispieltext Brief: Teil 1 Thank you for your last letter which I enyoyed very much. I‘m sorry to tell you, that it is impossible for us to come to England this year. Maybe it is possible next year. Probably we even can‘t go to Italy. The reason for this is that my father had a serious accident on his way back from the factorer where he works
Beispieltext Brief: Teil 2 He‘ll have to stay in the clinic for at least eight weeks. Isn‘t that terrible? Probably you are able to come to us, couldn‘t you? It would really nice if you can arrange it. I think it would be your first trip to Germany. You will really enjoy it. I must finish now. I hope that you will write soon By for now Love. Name
Inhalt Requested Info: Did you have a good time with your aunt? Are you going to Florence and Romey? Are you still coming to stay with us in the summer? Is there anything you would really like to do or anywhere you you‘ve always wanted to go? Do you want to come with me (my school) How is your new English teacher?
Inhalt Briefantwort Missing info: Did you have a good time with your aunt How‘s your new teacher?
Fehleridentifikation 1 Thank you for your last letter which I enyoyed very much. I‘m sorry to tell you, that it is impossible for us to come to England this year. Maybe it is possible next year. Probably we even can‘t go to Italy. The reason for this is that my father had a serious accident on his way back from the factorer where he works
Fehleridentifikation 2 He‘ll have to stay in the clinic for at least eight weeks. Isn‘t that terrible? Probably you are able to come to us, couldn‘t you? It would really nice if you can arrange it. I think it would be your first trip to Germany. You will really enjoy it. I must finish now. I hope that you will write soon By for now Love. Name
Fehlerinterpretation 1 Fehler Typ Stufe enyoyed spelling -(slip) you, -- we even can‘t syntax 1 factorer choice 2
Fehleridentifikation Fehler Korr Stufe the clinic hospital 1 couldn‘t you aren‘t 2 would really would be.. 1 can arrange could -- (J.S) You will ..enjoy would 1
Rubric-based evaluation In the classroom, a rubric is a set of criteria and standards (linked to learning objectives) that is used to grade a student assessment (paper, project, essay, etc). en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubrics_(education
Steps in Rubric Development Steps in Rubric Development • Determine learning outcomes • Keep it short and simple (Include 4 - 15 items; use brief statements or phrases) • Each rubric item should focus on a different skill • Focus on how students develop and express their learning • Evaluate only measureable criteria • Ideally, the entire rubric should fit on one sheet of paper • Reevaluate the rubric (Did it work? Was it sufficiently detailed?)
Terms to use in scoring levels • Needs improvement... Satisfactory... Good... Exemplary • Beginning... Developing... Accomplished... Exemplary • Needs work... Good... Excellent • Novice... Apprentice... Proficient... Distinguished • Numeric scale ranging from 1 to 5, for example
Rubric categories: letter writing Sentences and paragraphs Grammar and spelling Content accuracy Ideas Lenth
Rubrics levels Ideas 4: Ideas were expressed in a clear and organizied fashion. It was easy to figure out what the letter was about 1: The letter seemed to be a collection of unrelated sentences. It was difficult to figure out what the letter was about
Rubric levels 3: Ideas were expressed in a pretty clear manner, but the organization could have been better 2: Ideas were somewhat organized, but where not very clear. It took more than one reading to figure out what the letter was about.