Theodore Roosevelt's Presidency (1901-1909): A Progressive Era of Reform and Change
130 likes | 253 Vues
Theodore Roosevelt's presidency marked a transformative period in American politics from 1901 to 1909. A Harvard graduate and former governor of New York, Roosevelt ascended to the presidency after the assassination of McKinley. He championed the Progressive philosophy, advocating for corporate control, consumer protection, and conservation, known as the "Three C's." His administration took significant steps, like mediating the 1902 coal strike and enforcing antitrust laws. However, his successor, Taft, struggled to maintain this progressive momentum, leading to a split in the Republican Party and paved the way for Woodrow Wilson's New Freedom.

Theodore Roosevelt's Presidency (1901-1909): A Progressive Era of Reform and Change
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 (Republican) “The credit belongs to the man who is actually in the arena, whose face is marred by dust and sweat and blood; who strives valiantly; who errs, who comes short again and again; who knows great enthusiasms; who spends himself in a worthy cause; who at best knows in the end the triumph of high achievement, and who at the worst, if he fails, at least fails while daring greatly, so that his place shall never be with those cold and timid souls who neither know victory nor defeat. “
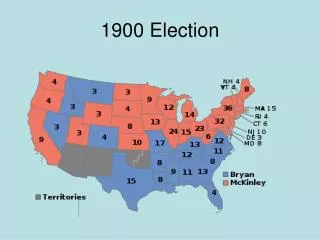
Rise to the Presidency • Former Harvard graduate, cowboy, police commissioner, NY assemblyman, Rough Rider • Nominated as Vice President to remove him from office as Governor of NY • McKinley’s assassination in 1901 by Leon Czolgosz - many Republicans worst nightmare
“That damned cowboy” • Strong beliefs / willing to compromise • Believed in direct action • Disliked the courts, frustrated by Congress • Saw Constitution as an obstruction • Greatly increased the power of the Executive Branch - power of the “bully pulpit”
Roosevelt – Reformer? Progressive philosophy - Three C’s (Control of Corporations, Consumer Protection, Conservation)
Control of Corporations • Progressive philosophy - “Square Deal” for the working man • 1902 Coal Strike - 1st time a president sided with labor • Northern Securities case - TR used the Sherman Anti-Trust Act to break up a monopoly (JP Morgan!) • Roosevelt distinguished between “good” and “bad” trusts – Gentlemen’s Agreement with Corporations • 1906 - Hepburn Act empowers the ICC to regulate the railroads
Consumer Protection • 1906 -Meat Inspection Act and Pure Food and Drug Act Response to Upton Sinclair’s the Jungle • Pure Food and Drug Act • Created the Food and Drug Administration • Required licensed physicians to sign prescriptions for medicine • Warning labels on addictive drugs
Conservation • Created 5 National Parks • Newlands Act - sold public land to build dams and canals to conserve water • 1906 - Antiquities Act - increased national forests 190 million acres • US Forest service - led by Gifford Pinchot prevented illegal use of public lands
William H. Taft • Progressives did not see Taft as a supportive of their policies – he abandons them • Still pushes 90+ anti-trust suits • Biggest suit – Standard Oil v. USA • Court breaks up Standard Oil • Adopts “Rule of Reason” – monopolies are allowed if they are reasonable • Suit against US Steel – biggest company, Roosevelt is outraged! • Final straw for Roosevelt – Taft’s Sec. of Interior Ballinger fires Pinchot over a dispute between trusts and corporations
New Freedom – New Nationalism New Freedom Wilson Use antitrust suits Against ALL trusts Triple Wall of Privilege: Banking, Trusts, Tariffs New Nationalism Roosevelt Use antitrust suits Against “bad trusts” Laws – not courts – Should protect people From harms caused by Corporations Activist Role Of the Federal Government Progressive Reform Use Antitrust suits
Woodrow Wilson - Democratic Progressivism Prime Minister style – • President should lead Congress in making laws • Wilson delivered message to Congress in person The Triple Wall of Privilege • Tariff – Underwood Tariff Bill cuts the tariff • Impact: new tax structure focused on domestic income • Banking – Federal Reserve Act • Impact: creates the Federal Reserve Board with currency control • Trusts – Clayton anti-trust (“labor’s Magna Carta”) • Impact: updated the Sherman Act • new weapons against the trusts • guaranteed union rights (strike rights, picketing)
Wilson’s Progressivism • More Progressive Reforms • Federal Farm Loan Act – credit to farmers at a low interest rate • Keating-Owen Act – limits child labor (struck down in Hammer v. Dagenhart, 1918) • Workingmen’s Compensation Act – disability payments to federal workers Limits of Wilson’s Reforms • African Americans had little influence over Wilson • Suffragettes were dismissed by Wilson