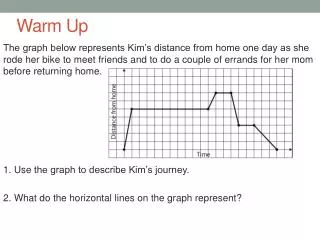
Warm-up
380 likes | 652 Vues
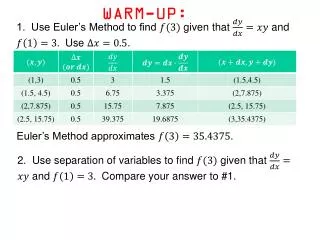
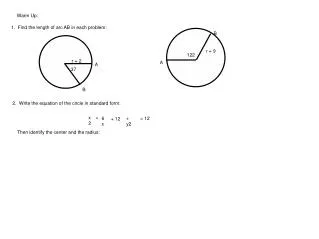
Warm-up. 1) Solve for x, y, and z. 2) Solve for x. 3) Solve for x. Today’s Agenda. Review of Chapter 12 Theorems 12.4 Secants angle measures segment proportions Next Class Review/Test Check Skyward. Missing Quizzes/Tests 1st. 12 Quiz

Warm-up
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm-up • 1) Solve for x, y, and z. • 2) Solve for x. • 3) Solve for x.
Today’s Agenda • Review of Chapter 12 Theorems • 12.4 Secants • angle measures • segment proportions • Next Class • Review/Test • Check Skyward
Missing Quizzes/Tests 1st • 12 Quiz • Sharlanae, Courtney, Lillian, Jordan, Bridger, Johnny, Abigail • 10 Test • Armin, Pouria, Jordan, • 10 Quiz • Armin, Abigail
Missing Quizzes/Tests 5th • 12 Quiz • Josi, Conner P, Nikol • 10 Test • Josi, Andrew, Nikol • 10 Test • Shelby • Check Skyward
Missing Quizzes/Tests 6th • Chapter 12 Quiz • Julian, Tanner C, Connor • Chapter 10 Test • Sam, Connor, Hunter • Chapter 10 Quiz • Coleman, Tanner R, Kolton • Check Skyward
Tangent Lines • A tangent to a circle is a line that intersects a circle at exactly one point. • The point of intersection is called the point of tangency.
Theorem 12-1 • If a line is tangent to a circle, then the line is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency.
Theorem 12.2 • Converse of 12.1 • If a line is perpendicular to a radius at its endpoint on the circle, then the line is tangent to the circle.
Theorem 12.3 • 2 segments tangent to a circle from a point outside the circle are congruent.
Theorem 12.4 • Within a circle or in congruent circles… • congruent central angles have congruent chords • Angle DOB Angle COA • DB CA
Theorem 12.4 • Within a circle or in congruent circles… • congruent chords have congruent arcs • DB CA • Arc DB Arc CA
Theorem 12.4 • Within a circle or in congruent circles… • congruent arcs have congruent central angles • Arc DB Arc CA • Angle DOB Angle COA
Theorem 12.5 • Within a circle or in congruent circles… • chords equidistant from the center are congruent • (side note) measure distance with perpendicular line • CL CM • XW ZY
Theorem 12.5 • Within a circle or in congruent circles… • congruent chords are equidistant from the center. • XW ZY • CL CM
Theorem 12.6 • In a circle, a diameter that is perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord and its arc.
Theorem 12.7 • In a circle, a diameter that bisects a chord (that is not the diameter) is perpendicular to the chord.
Theorem 12.8 • In a circle, the perpendicular bisector of a chord contains the center.
Inscribed Circle • Inscribed Angle • Angle whose vertex is on a circle and whose sides are chords. • Intercepted arc • Arc created by an inscribed angle.
Theorem 12.9-Inscribed Angle Theorem • The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. • ABC = ½AC
Corollaries to the Inscribed Angle Theorem • 1) Two inscribed angles that share an intercepted arc are congruent. • 2) An angle inscribed by a semicircle is a right angle.
Corollaries to the Inscribed Angle Theorem • 3) The opposite angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle are supplementary. • angle N + angle O = 180˚ • angle P + angle M = 180˚
Theorem 12.10 • The measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a chord is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Review • Identify the Following • Chord • Diameter • Secant Line
Secant Lines • A secant line is a line that intersects 2 sides of a circle. • Is the diameter a secant?
Theorem 12.11 Part 1 • The measure of an angle formed by 2 lines that intersect inside a circle is the average of the 2 arcs. • angle 1 =
Example 2 • Find the value of x.
Theorem 12.11 Part 2 • The measure of an angle formed by 2 lines that intersect outside a circle is the difference of the arcsdivided by 2. • x is the bigger angle
Example 2 • Find the value of x.
Theorem 12.12 Part 1 • If two chords intersect, then .
Example 3a • Find the value of x.
Theorem 12.2 Part 2 • If 2 secant segments intersect, then (w + x)w = (z + y)y
Example 3c • Find the value of x.
Theorem 12.2 part 3 • If a secant segment and a tangent segment intersect, then (y + z)y = t2
Example 3b • Find the value of z.
Assignment • 12-4 Worksheet • Turn in CRT Review • Extra Credit • pg 707 #1 – 21 all skip 5 • Check off 12-3