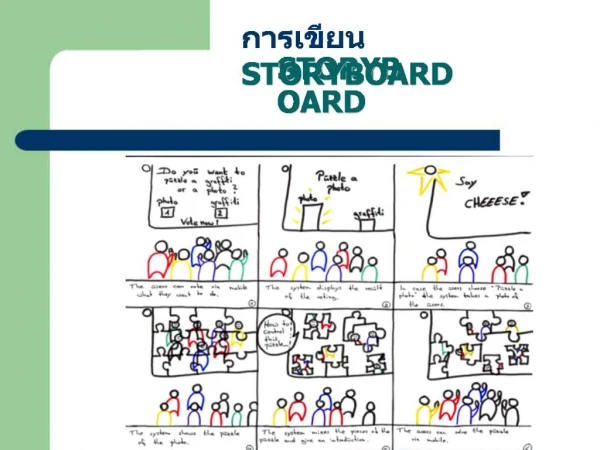
Storyboard for
180 likes | 444 Vues
Does audit quality matter?. Storyboard for. …clear thinking. By completing this module you will be able to: Explain why audit quality is important for practitioners as well as regulators and standard-setters Describe recent audit quality initiatives

Storyboard for
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Does audit quality matter? Storyboard for
By completing this module you will be able to: Explain why audit quality is important for practitioners as well as regulators and standard-setters Describe recent audit quality initiatives Describe and evaluate the constituent elements of audit quality as set out in IAASB’s Framework for Audit Quality At the end, you can visit useful Internet sites on a “Web Ride” Lecturer: Katharine Bagshaw Learning time: approx. 15 minutes How to use this learning module? - Click on "Help" in the Table of Contents (TOC) Does audit quality matter? Photo of author
Why do standard-setters spend so much time on audit quality? Audit quality drivers include: recognition that audit quality requires more than auditing standards combined effects of audit exemption, competition among firms and the burden of compliance financial crises: assuming recent audits were conducted properly, what is the value of audit? Is ‘audit quality’ really so important? Graphic: [a dense forest]
The Audit Quality Forum first convened by ICAEW in 2004 to bring together investors, preparers, regulators and auditors The FRC’s Audit Quality Thematic Reviews – first publication on materiality published Dec 2013 The IAASB’s Audit Quality project finalised Dec 2013: - inputs, processes, outputs, interactions and contextual factors - engagement, firm and national levels. Audit quality initiatives Graphic: [ a pair of secateurs]
The values, ethics and attitudes of auditors The knowledge, skills, and experience of auditors and the time allocated to perform the audit Elements of audit quality: inputs Graphic: [ an entrance / entrance sign]
Engagement and firm levels: methodologies, IT, file reviews and engagement quality control reviews National level: standards need to make objectives clear, audit inspectors need to consider quality issues, systems needed to investigate allegations of audit failure. Elements of audit quality: processes Graphic: [ a clockwork mechanism]
Engagement level outputs include audit reports on financial statements, to those charged with governance and management, to financial and prudential regulators Entity outputs having a bearing on audit quality includeaudited financial statements - it is easier to audit a well-prepared set - and reports from those charged with governance National levelrequirements for larger audit firms to prepare transparency reports Audit inspection reports by regulatorsproviding individual firm or aggregated information Elements of audit quality: outputs Graphic: [ an exit / exit sign]
Interactions that influence audit quality are between: auditors management those charged with governance financial, prudential and audit regulators financial statement users All part of the financial reporting supply chain. Elements of audit quality: interactions Graphic: [part of the Underground map]
Contextual factors affecting audit quality include: the financial reporting framework and related laws and regulations business practices, commercial law, the corporate governance regime and regulation information systems and the financial reporting timetable the litigation environment and broader cultural factors. Elements of audit quality: contextual factors Graphic: [archery target]
Numerous references to smaller audits include: the fact that management may value business advice – independence issues communications between auditors and Those Charged With Governance - more frequent and less formal informal corporate governance structures a lack of distinction between management and Those Charged With Governance partner control over the culture of a firm which can be a strength or a weakness technical support needed from outside the firm A shorter guide to audit directed at smaller entities may be produced References to smaller firms in the Framework Graphic: [microscope]
The key things to remember from this module are that audit quality: and quality control are not the same is of increasing interest to regulators is important to firms performing audits as a way of resisting fee pressures, and to distinguish the firm from other firms. Summary Graphic: [standard summary graphic]
Please select the correct answer(s) and then click on “Submit” Which of the following statements are true? Auditors are required to comply with the Framework for Audit Quality (UK and Ireland) for the audit of financial statements commencing on or after 15 Dec 2014 Auditors are not required to comply with the Framework for Audit Quality Compliance with the Framework for Audit Quality (UK and Ireland) is required for the auditors of listed entities and other entities that apply the UK Corporate Governance Code Auditors required to prepare annual reports under the EU’s Transparency Directive are required to comply with the Framework for Audit Quality (UK and Ireland) or explain why they have not done so Question 1
Please select the correct answer(s) and then click on “Submit” Which of the following statements are true? The constituent elements of the IAASB’s Framework for Audit Quality are inputs, processes, outputs and interactions Quality audits involve auditors exhibiting appropriate values, ethics and attitudes and being sufficiently knowledgeable, skilled, and experienced and having sufficient time to them to perform the audit work Audit quality operates at the engagement level, the firm level and at national level The interactions that influence audit quality are between auditors, management, those charged with governance, regulators and financial statement users Question 2
Please select the correct answer(s) and then click on “Submit” Which of the following statements are true? Audit quality is influenced by the inputs, processes, outputs and interactions described in IAASB’s Framework for Audit Quality but the Framework alone is insufficient to evaluating the quality of an audit A quality audit requires compliance with auditing standards and legal, ethical and other regulatory requirements, among other things Audit quality is best achieved in an environment where there is support from and appropriate interactions among participants in the financial reporting supply chain Compliance with IAASB’s Framework for Audit Quality is an allowed alternative to compliance with IAASB’s ISQC 1 on quality control Question 3
You have finished this module and acquired a basic understanding of audit quality issues If you answered all of the questions in the Quiz correctly, you can print out your personal certificate by clicking on the link Thank you for your attention! Finish Graphic: [standard finish graphic]