WAN Technology
330 likes | 927 Vues
Chapter 4. WAN Technology. Wide Area Network Technology. Prepared By. Lec, Heng Pheakna. I. What is WAN ? . A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunication network that covers a broad area (i.e., any network that links across metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries).

WAN Technology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 4 WAN Technology Wide Area Network Technology Prepared By. Lec, Heng Pheakna
I. What is WAN ? A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunication network that covers a broad area (i.e., any network that links across metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries).
Business and government entities utilize WANs to relay data among employees, clients, buyers, and suppliers from various geographical locations. In essence this mode of telecommunication allows a business to effectively carry out its daily function regardless of location
II. Why we use WAN? Because leased lines are expensive, many businesses that require a WAN use an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to provide WAN access instead. In this case, each LAN in the WAN communicates through a standard digital subscriber line (DSL) account. The DSL Internet account uses an existing telephone line while sharing that line with the telephone.
III. Why we use WAN? Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets. Packet switching features delivery of variable-bit-rate data streams (sequences of packets) over a shared network.
Packet switching contrasts with another principal networking paradigm, circuit switching, a method which sets up a limited number of dedicated connections of constant bit rate and constant delay between nodes for exclusive use during the communication session. In case of traffic fees (as opposed to flat rate), for example in cellular communication services, circuit switching is characterized by a fee per time unit of connection time, even when no data is transferred, while packet switching is characterized by a fee per unit of information.
IV. WAN Virtual Circuits A virtual circuit is a logical circuit created within a shared network between two network devices. Two types of virtual circuits exist: switched virtual circuits (SVCs) and permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). SVCs are virtual circuits that are dynamically established on demand and terminated when transmission is complete. Communication over an SVC consists of three phases: circuit establishment, data transfer, and circuit termination. The establishment phase involves creating the virtual circuit between the source and destination devices.
PVC is a permanently established virtual circuit that consists of one mode: data transfer. PVCs are used in situations in which data transfer between devices is constant. PVCs decrease the bandwidth use associated with the establishment and termination of virtual circuits PVCs are generally configured by the service provider when an order is placed for service.
V.Dialup Service Offer Dialup services offer cost-effective methods for connectivity across WANs. Two popular dialup implementations are dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. DDR is a technique whereby a router can dynamically initiate a call on a switched circuit when it needs to send data. In a DDR setup, the router is configured to initiate the call when certain criteria are met, such as a particular type of network traffic needing to be transmitted. When the connection is made, traffic passes over the line. The router configuration specifies an idle timer that tells the router to drop the connection when the circuit has remained idle for a certain period.
VI. WAN Devices. There are specially designed network devices that are used to interconnect LANs. Configuring, installing and maintenance of this devices requires expert skills by skilled technicians for the management of the organization's network. These devices are specific to WAN environment, and they are:
Modems Modems enables digital data to be sent over an analogue medium during transmission and receiving of information A voice band modem converts the digital signals produced by a computer – the 1s and 0s- into voice frequencies that can be transmitted over the analogue lines of the telephone network. On the other side of the connection, another modem converts the sounds back into a digital signal for input to a computer or network connection
CSU/DSU Channel Service Unit / Data Service Unit CSU/DSU are combined piece of equipment used for monitoring clocking and frame synchronization on a line. It also performs error detection at the physical layer, It could be called a Modem sort of.
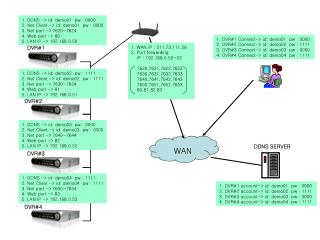
Access server Concentrates dial-in and dial-out user communications. An access server may have a mixture of analogue and digital interfaces and support hundreds of simultaneous users.
WAN Switch A multi-port internetworking device used in carrier networks. These devices typically switch traffic such as ATM, and operate at the Data Link layer of the OSI reference model. Public switched telephone network switches may also be used within the cloud for circuit-switched connections like Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or analogue dialup.
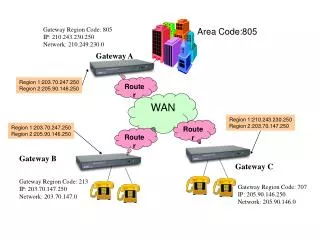
Router A Router Provides internetworking between the LANs, and WAN access interface ports that are used to connect to the service provider network. These interfaces may be serial connections or other WAN interfaces. With some types of WAN interfaces, an external device such as a DSU/CSU or modem (Analogue, Cable, or DSL) is required to connect the router to the local point of presence (POP) of the service provider.
Core Router A router that resides within the middle or backbone of the WAN rather than at its periphery. To fulfil this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the WAN core, and it must have the ability to forward IP packets at full speed on all of those interfaces. The router must also support the routing protocols being used in the core.
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communications standards for simultaneous digitaltransmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the traditional circuits of the public switched telephone network.