Classical Conditioning
240 likes | 509 Vues
Classical Conditioning. Unit 3- Module 14 Notes. Definitions. Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Classical Conditioning Type of learning in which a stimulus gains the power to create a response Stimulus

Classical Conditioning
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Classical Conditioning Unit 3- Module 14 Notes
Definitions • Learning: • A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience • Classical Conditioning • Type of learning in which a stimulus gains the power to create a response • Stimulus • Anything in the environment that one can respond to • Response • Any behavior or action
Classical Conditioning • There are four main components to classical conditioning: • Unconditioned Stimulus (US) • Unconditioned Response (UR) • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) • Conditioned Response (CR)
Classical Conditioning • Unconditioned Stimulus (US) • Stimulus that triggers an automatic and reflexive response • Classical conditioning CANNOT happen without an US • In the shower example, what is the US? • Hot water
Classical Conditioning • Unconditioned Response (UR) • The automatic response to the US • Relationship between the US and UR is reflexive and automatic- it is NOT learned • In the shower example, what is the UR? • Jumping out of the way of the hot water
Classical Conditioning • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) • A previously neutral stimulus that , through learning, gains the power to cause a conditioned response • Before classical conditioning takes place, the stimulus is considered a neutral stimulus • In the shower example, what is the CS? • The word “Flush”
Classical Conditioning • Conditioned Response (CR) • The response to the Conditioned Stimulus • Is the same behavior that is identified as the UR • In the shower example, what is the CR? • Jumping out of the way of the hot water
Classical Conditioning • Two basic processes in classical conditioning: • Acquisition • Process of developing a learned response • Occurs when a neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with a US (called a trial) • In the shower example, how would we know that acquisition has taken place? • When the word “Flush” is said and the person jumps out of the way without the hot water being present
Classical Conditioning • Extinction • Diminishing of a learned response after repeated presentation of the CS by itself • How could the CR of jumping out of the way in the shower become extinct? • Repeatedly yell “Flush” (CS) without actually flushing the toilet • Since water wouldn’t get hot, learner wouldn’t react to the CS
Classical Conditioning • Two more terms: • Generalization • Producing the same response to two similar stimuli • Discrimination • Ability to distinguish between 2 signals or stimuli and produce different responses
Classical Conditioning • Aaron was sitting on a park bench licking a lollipop when he got stung in the ear by a bee. The sting produced a great deal of pain and, as a result, fear of bees. After the incident, Aaron began experiencing fear whenever he heard the buzzing sound of a bee.
Classical Conditioning • In that scenario, what is the: • US? • Pain from the sting • UR? • Fear of bees • CS? • Buzzing of bees • CR? • Fear of bees
Classical Conditioning • In the previous scenario, how might we observe generalization? • If Aaron displayed fear of all buzzing insects • If Aaron feared all buzzing insects at first, what would need to happen for us to observe discrimination? • Aaron showed the ability to not be afraid of buzzing insects that did not produce painful stings
Classical Conditioning Experiment #1 • Observe the demonstration • When complete, jot down the following: • US, UR, CS, CR, Generalization (if any), Discrimination (if any), Extinction (if any), Acquisition (if any) • Then, we will discuss as a class
Classical Conditioning Experiment #1 • Observe the demonstration • When complete, jot down the following: • US, UR, CS, CR, Generalization (if any), Discrimination (if any), Extinction (if any), Acquisition (if any) • Then, we will discuss as a class
Classical Conditioning • In the famous “Baby Albert” experiment, identify the: • US • UR • CS • CR • Generalization
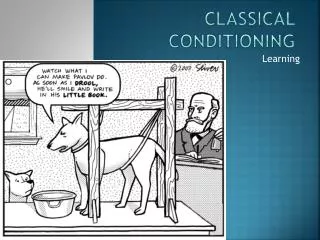
Classical Conditioning • Ivan Pavlov’s Experiment • Pavlov was conducting an experiment on the role of saliva on digestion- the results of his experiment, however, became a benchmark in behavioral psychology!
Classical Conditioning • Pavlov’s experiment • The initial results of the experiment were a success- the dog salivated when the meat was introduced • After a period of time, however, the dog became familiar with the procedure and began to salivate before the meat arrived • Pavlov decided to change his experiment and see if he could train the behavior of the dog by causing it to salivate to the sound of a tuning fork rather than the presence of meat
Classical Conditioning • Using what we have discussed, CREATE Pavlov’s experiment • Identify the US, UR, CS, CR • Identify how acquisition would be produced • Identify how extinction would be observed