Fundamentals of Ionic Polymerization in Chemical Engineering
170 likes | 216 Vues
Explore cationic and anionic polymerization processes at Konkuk University, including initiators, monomers, and applications in polymer synthesis. Discover the complexities and applications of ionic polymerization in various industries.

Fundamentals of Ionic Polymerization in Chemical Engineering
E N D
Presentation Transcript
20 08 Nov. 7, 2008 제6장Ionic Polymerization Department of Chemical Engineering Konkuk University
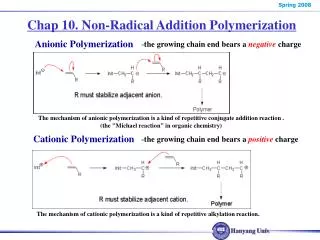
Cationic Polymerization • 이온 중합 분류 Anionic Polymerization Ionic polymerization • i)More complex than free radical polymerization • ii) Application in ring opening polymerization of cyclic ethers, lactams & lactones • Propagating chain end is polar • Occurs in solution • Monomers should have substituent groups for stabilizing carbocations or anions
I. Cationic Polymerization 1. Cationic Initiators Initiation starts by addition of an electrophile to a monomer molecule In cationic chain polymerization, the propagating species is a carbocation. + + + E CH2=CR2 ECH2CR2 Commercial polymers synthesized by Cationic polymerization: Polyisobutylene & polybutenes Isobutylene-isoprene copolymer polyvinylethers
Types of initiation Protonic acids Lewis acids Metal halides
양이온 중합 (1) 개시제 (Protonic acid) BCl3
Lewis acids need water or other cation source to form electrophilic species to initiate polymerization. Ex: i) BF3 with water ii) Aluminium chloride with an alkyl chloride BF3 H2O HOBF3 H AlCl3 RCl AlCl4 R - + + - + +
Lewis 산을 개시제로 사용 시: 공촉매 (물, 메탄올 등) 필요
공촉매: H+공여형: H2O, Alcohol, Acid Carbonium 형성형: Alkyl halide Ex) Metal halide는 공촉매로 부터의 불안정한 Ion Pair를 안정한 Ion Pair(AlCl3-OH)-등으로 바꿈 개시, 성장 반응 용이
In cationic initiation, the rate of addition to aliphatic monomers is (CH3)2C CH2 > CH3CH CH2 > CH CH2 Of these three monomers, isobutylene has the carbocation stability for cationic polymerization Electron donating groups are needed as the R groups because these can stabilize the propagating species by resonance.
Transfer with termination • Polymerization must be carried out at low temp. (-78C), because carbenium salts are extremely reactive. • Number of side reactions can occur.
Example of Commercial Cationic Polymers Cationic polymerization of Polyisobutylene (PIB) Temp of polymerization -100 oC to -30 oC high rate of heat is released (cationic is very rapid, faster than other polymerization methods) Rp should be lowered to control the reaction Precipitation occurs as polymer is generated