Earth’s Changing Crust
230 likes | 552 Vues
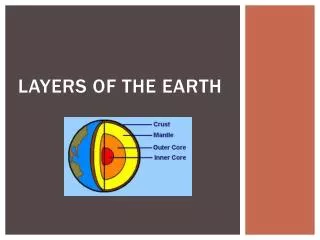
Earth’s Changing Crust. Geologist. Scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth “ geo” refers to the earth. Crust. Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin The outer shell of the Earth is called the CRUST. Mantle.

Earth’s Changing Crust
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geologist • Scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth • “geo” • refers to the earth
Crust • Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin • The outer shell of the Earth is called the CRUST
Mantle • Layer of hot, solid material between the crust and the core • The next layer is called the MANTLE
Core • The 2 innermost layers of the Earth • Outer core • (liquid) • Inner core • (solid)
Earthquakes ~Caused by the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface ~Earth’s crust is constantly moving
Faults • A break in Earth’s crust • Rocks on both sides can move up, down or sideways • Movement along faults form mountains and valleys • Caused by • Compression • Tension • Shearing
What causes a fault? • Compression • Tension • Shearing
Different types of faults • 1. Strike-slip faults ( caused by shearing) • Rocks on either side slip past each other • Slide past each other sideways, not up or down
2. Normal fault (caused by tension) • It’s at an angle so one block of rock hangs above and one hangs below
3. Reverse fault ( caused by compression) • The blocks move in opposite directions • Formed part of the Appalachian Mountains
What are 3 kinds of faults? • Strike-slip • Normal • Reverse • What kind of fault doesn’t move up or down? • Strike-slip
Richter Scale Rates the size of the seismic waves • Information comes from a seismograph (Chinese) • A seismograph is the machine used to measure the movement of the Earth’s crust.
Plate tectonics - A theory that pieces of the Earth’s mantle are in constant, slow motion • tec·ton·ic/tekˈtänik/ - Adjective: 1.Of or relating to the structure of the earth's crust and the large-scale processes that take place within it.
Magma • Hot, molten rock deep below Earth’s surface
Lava • Magma that reaches the Earth’s surface • Magma come from a Greek root which means “thick ointment” • . Magma and lava are identical substances • One is above the surface of the Earth and the other is below the surface of the Earth.
Weathering • The breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces
Erosion • The picking up and carrying away of pieces of rock
How do weathering and erosion work together to shape Earth’s surface? • Weathering breaks down Earth surface and erosion carries away the broken-down pieces. • What are 2 kinds of weathering? • Physical • Chemical
Deposition • The dropping off of bits of eroded rock
Meteorite • A chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface, such as Earth