Understanding Pointers and Arrays in C Programming: A Comprehensive Guide
110 likes | 265 Vues
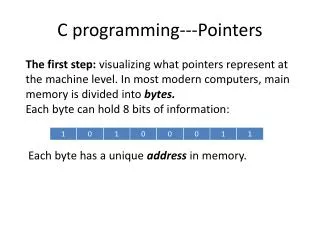
This guide delves into the intricate relationship between pointers and arrays in C programming. It covers how arrays can be accessed using both array subscript notation and pointer/offset notation, illustrated with examples. For instance, the array 'b' can be referenced as 'b[0] = 10' or through pointer notation as '*(b + 0) = 10'. It also examines pointer subscript notation, such as 'bPtr[0] = 10', and demonstrates how pointers can facilitate array manipulation. Additionally, sample program outputs are included to enhance understanding.

Understanding Pointers and Arrays in C Programming: A Comprehensive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pointers in C The relationship between pointers and arrays
Array b printed with: Array subscript notation b[ 0 ] = 10 b[ 1 ] = 20 b[ 2 ] = 30 b[ 3 ] = 40 Pointer/offset notation where the pointer is the array name *( b + 0 ) = 10 *( b + 1 ) = 20 *( b + 2 ) = 30 *( b + 3 ) = 40 Pointer subscript notation bPtr[ 0 ] = 10 bPtr[ 1 ] = 20 bPtr[ 2 ] = 30 bPtr[ 3 ] = 40 Pointer/offset notation *( bPtr + 0 ) = 10 *( bPtr + 1 ) = 20 *( bPtr + 2 ) = 30 *( bPtr + 3 ) = 40 Program Output
fig07_21.c (Part 2 of 2) Program Output string1 = Hello string3 = Good Bye