Antibiotics – Part 1: Chapter 38
160 likes | 794 Vues
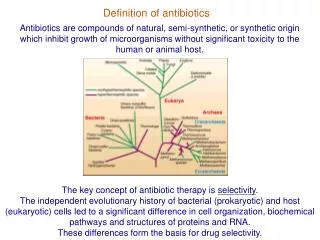
Antibiotics – Part 1: Chapter 38. What is an antibiotic?. A medication that kills bacteria or slows their growth Are classified based on their based on their chemical structure Some common classes are sulfonamides, penicillins, cephalosporins , carbapenems ,

Antibiotics – Part 1: Chapter 38
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is an antibiotic? A medication that kills bacteria or slows their growth Are classified based on their based on their chemical structure Some common classes are sulfonamides, penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams, macrolides & tetracyclines Act against types & species of different microorganisms that are infectious
Bacterial Infection? • Microorganisms invade & multiply within a person and these signs & symptoms are commonly seen: • Fever • Chills & Sweats • Redness • Pain • Swelling • Fatigue • Weight loss • Increased WBC’s • Pus
How do I know which antibiotic to take? • When a patient presents these signs and symptoms, they should seek medical attention • To begin the treatment of a bacterial infection, a broad spectrum antibiotic may be given • A culture which will identify the specific microorganism as either gram-positive or gram-negative should be ordered • Based on the results, an appropriate antibiotic may be prescribed to treat the unique microorganism that caused the infection