Data Replication Strategies
530 likes | 846 Vues
Data Replication Strategies. The Bane of Business Disruption. Stop production! It’s backup time. Executive Summary.

Data Replication Strategies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Data Replication Strategies The Bane of Business Disruption Stop production! It’s backup time
Executive Summary Do not risk conducting business without a Business Continuation Plan… …employing modern data replication technology you do not need to stop business processing to back up data or to install the additional disk storage.
Overview • What is Data Replication Technology? • Why is it important? • How and when did it come about? • How can we use it? • The Benefits…
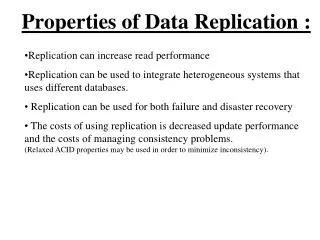
What Is Data Replication Technology? • Software and hardware for making additional copies of existing data…to improve data availability.
Why is Data Replication Important? • Data Replication is a solution for protection against loss… • Data Replication is key to improving data availability for Business Continuance.
How Improve Data Availability? • Development and Testing • “Disposable” Copy for experimenting • Improve Production Processing • “Duplicate” Copy for parallel access • Business Protection / Business Continuance • “Backup” Copy as insurance against loss
Business Continuation…More than Disaster Recovery • Apply Basic Principles • Consider e-Business Requirements • 24x7x365 Availability • Non-Stop Operations • Employ Instant technology
Where Does the Pressure Come From? “e-Business extends direct consumer access to existing real-time business systems”
You Don’t Need A Disaster To Have A Disruption! • Natural Disasters • Site Destruction/Disruption • Fires, Power and Communications Failure • Mechanical Equipment Failure • Processor, Disk and Network Hardware • Software Failure • Operating System and Application • Human Error • One Third of All Data Loss is Caused by Human Error • Scheduled downtime… • Backup, New Equipment…
How Much Does Disruption Cost? • Lost opportunity… • Securities Trading $6.5 million per hr • Intel Web Site Sales $275,000 per hr • Cable Home Shopping $113,000 per hr • Airline Reservations $ 89,000 per hr • Cellular Service Activation $ 41,000 per hr • Fraud Exposure… Credit Cards $2.6 million per hr
WHERE IS THE DATA?Modern disk storage… Forty-five years old Thirty-eight years old Thirty years old Twenty-five years old
A Forty-Five Year Old Invention? September 13, 1956, the first RAMAC
Thirty-Eight Year Old Interconnections and a Thirty Year Old Controller..
Innovation Continued…! • Disk storage capacity grew through the 1970s and 80s from 10 MBs to 100 MBs to 1000 MBs, gigabytes and terabytes…
ATwenty-Five Year Old Scheme Raid Structures • 1978 IBM patent for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. • 1987 University of California at Berkeley “Inexpensive” Disks
Software Solutions AutomatedBACKUP AND RECOVERY • Three approaches to backup • Two reduce time by limiting the amount of data. • One automates the solution.
Automated Software SolutionsCUT BACKUP TIME 50 TO 80 % (Daily INCREMENTAL) Weekend Full Volume Backup Image Daily Incremental Backup Image
ESS 2105 (SHARK) Lighting RVA-X83 10 Years ago it began coming together RAID Storage began Replacing SLEDS, SHARED VIRTUAL ARRAY SVA
Intelligent Storage • 1987@ IBM 3990-3 (Dual Copy) • 1992/1993@ IBM 3990-6 (Concurrent Copy, PPRC, P/DAS and XRC ) • 1994@ Symmetrix (Mirror Protection™, , EMCCopy and SRDF) • 1995@ StorageTek IceBerg (SnapShot Copy™) • 1996/1997/1998@ IBM RVA (SnapShot Copy™) EMC Symmetrix (TimeFinder™) Hitachi (DataPlex™, ShadowImage and NanoCopy) • 1999@ IBM Shark (FlashCopy) @ Date approximate to depict time-line development
The Start of it AllLocal Volume Mirroring 1987 Dual Copy
Cache Side File for Updated Tracks Introducing Point-in-Time-Copy 1992 Concurrent-Copy
PPRC, SRDF, HRC (and P/DAS) 1993/1994 Remote Dual Copy
StorageTek SnapShot™ Point-in-Time Copy Raid 5 1995 IceBerg Raid 5 & SnapShot Copy
ICEBerg SnapShot Copy Technology FTT for 01AC FDT TNT Addr Type Size 01AC 3390 3339 01AD 3390 3339 … … 0248 3380 2655 CCHH Pointer 002F0E 002F0F Use count Ptr 2 1 ... FTT for 01AD CCHH Pointer 002F0E 002F0F
EMC TimeFinder™Point-in-Time Copy 1997 Symmetrix BCV & TimeFinder
Hitachi Point-in-Time Copy HS-DataPlex ShadowImage 1998 ShadowImage & HMRCF
IBM FlashPoint-in-Time Copy 1999 ESS 2105 SHARK & FlashCopy
How Can Data Replication be Useful? Data Replication is a strategic technology, to eliminate… • Long interruptions for backup... • Unacceptable recovery times… • Production delays to copy data… • Hard downtime to install new disks…
Impediments to Data Replication Being Useful • Backup not on removable media • Point-in-time hardware produce exact duplicates • MVS does not allow duplicates online • Conventional backup can not read offline volumes • Re-labeling to bring volumes online destroys catalog access to data and means special restore procedures
Hardware and SoftwareWorking Together • Non-Disruptive e-Business Backup • Instant e-Business Recovery • Backup/Restore Data Reduction • Outboard/Host-Less Data Movement • Install Disk Storage w/ no downtime • Non-Disruptive Disk Load Balancing It's not magic, we do it with mirrors !
Automate e-Business Protection INSTANT Technology Software • Identify change files—Manage Backup Selection • Use InstantTechnology Point-in-Time Disk Backup • Provide Non-Disruptive Tape Backup • Interface with Tape Management Systems • Keep familiar offsite DR procedures the same • Provide InstantRestore for onsite auto recovery
INSTANT INCREMENTAL A Backup Solution with Greater Savings • Reduce Business Disruption with SnapShot, TimeFinder, ShadowImage or FlashCopy • INSTANT Incremental is non-disruptive • Non-Disruptive incremental cut tape usage half to 75%… Only backup what is changed
INSTANT INCREMENTALis Easy! • Use InstantTechnology point-in-time disk backup • Record location of the InstantTechnology Backup- Restores are then immediately available • Non-Disruptively dump to tape from the InstantTechnology point-in-time disk backup …after the non-disruptive tape backup keep the InstantTechnology Backup disk for InstantRestore
InstantTechnology BackupSnapShot/TimeFinder ShadowImage/FlashCopy
InstantRecovery • No Change to Existing Procedures • Local InstantRestore Datasets (Volumes) from Incremental or (Volume) InstantTechnology Backup disk • z/OS, OS/390 and System Managed Storage Compatible • Easy-To-Use, Familiar Tape Restore for Offsite Recovery
M-vol(S) R-vol(S) M-vol(T) R-vol(T) Local Remote Real or Virtual Comprehensive Business Protection Local Business ContinuationRemote Disaster Recovery • Local Business Continuation - (Local) Point-in-Time Backup • Remote Disaster Recovery - Real-Time Protection • (Remote) Secondary Location Point-in-Time Backup
Instant Space Management for Continuous Business Operations “INSTANT” Technology Utilities • (Server-Less Space Management) • Reclaiming Wasted Disk Space • Reducing Disk Volume Fragmentation • (Server-Less Data Replication) • Dataset and Volume Copy & Move • (Non-Disruptive Data Relocation) • Relocate Data to Install New Hardware • Relocate Data to Balance and Eliminate Hot Spots
Reorganize in Seconds Data Replication + DiskCompaktion… InstantCompaktion • Disk Reorganization in Seconds • Employs SnapShot or EMCCopy • Arranging the Disk to Match its VTOCWithout Reading or Writing any Data Tracks • Reducing Disk Fragmentation in an Instant • Consolidating Free Space • Combining Dataset Extents • Releasing Unused Tracks
SVA Compressed Data The POWER of RE-PACKAGING:SVA 9500, V960 with Virtual Power Suite(HSDM™ )… High Speed Data Mover
I/O REDIRECTION Another Aspect of Data Replication • INNOVATION FDRPAS (2001) • EMC CopyCross (2001) • StorageTek ExHPDM (1999) • Fujitsu Softek (Amdahl) TDMF (1996)
Fujitsu Softek (Amdahl) TDMF I/O REDIRECTION • 1996 - Transparent Data Migration Facility Migrate Data Without Interrupting Applications
ExHPDMPhysical Tape FDRTape DUMP StorageTek ExHPDMI/O REDIRECTION • 1999 - Extended High Performance Data Mover Redirect multiple data streams to a single tape transport
FDRINSTANT HSDM and ExHPDM Integration • Employing HSDM and ExHPDM, together ABR backups complete in 1/3 the time… • Employing SnapShot even that time is non-disruptive ExHPDMTape Format FDRDUMP Format Data in Compressed Hardware Format
FDRTape DUMP CopyCrossLogical Tape EMC CopyCross I/O REDIRECTION • 2001 - Transparently redirecting tape data to disk
FDRPAS™Non-Disruptive (Plug and Swap)Disk Install and Load Balancing • Add disk storage • Eliminate hot spots • Interactive, Easy-to-Use, Non-Disruptive • Create Point-in-Time Disk Backup • Preserve or Reserve Disk Capacity • Interactively Manage Data Relocation,Volume Condition and System I/O Activity