8.1 Exponential Growth 8.2 Exponential Decay
100 likes | 798 Vues
8.1 Exponential Growth 8.2 Exponential Decay . Exponential Function. An exponential function has a positive base other than 1. The general exponential function is. The graph of y = b x. Graph Exponential function.tii.

8.1 Exponential Growth 8.2 Exponential Decay
E N D
Presentation Transcript
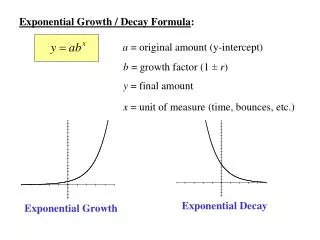
Exponential Function An exponential function has a positive base other than 1. The general exponential function is
The graph of y = bx GraphExponential function.tii Asymptote – a line that a graph approaches as you move away from the origin. ( The graph never touches the line.) If b is greater than 1 the graph is an exponential growth. b > 1 If b is greater than 0 but less than 1 the graph is an exponential decay. 0 < b < 1 ( A reflection in the y direction.)
The graph of y = abx-h + k GraphExponential function.tii If a is negative the graph will reflect in the x direction. The absolute value of a changes the y- intercept. The h shifts the graph horizontally. (left or right) The k shifts the graph vertically. (up or down)
Exponential Growth Model Instead of x, t is the variable. (1+r) is called the growth factor. a is the initial amount. y is the amount after t years.
Exponential GrowthCompound Interest A is the balance. P is the principal deposited in an account. r is the interest rate changed to a decimal (% 100). n is the number of times the interest is compounded in a year. Annually n = 1 Semiannually n = 2 Quarterly n = 4 Monthly n = 12
Compound Interest Problem You deposit $500 in an account that pays 3% interest. Find the balance after 2 years if the interest is compounded quarterly. A = ? P = $500
Exponential Decay Model y is the quantity after t years. t is the variable. a is the initial amount. (1-r) is the decay factor.
Exponential DecayDepreciation You buy a new car for $22,000. The value of the car decreases by 12.5%. What is the value of the car after 4 years. y = ? a = $22,000