Chapter 2. The PHISICAL LAYER
250 likes | 409 Vues
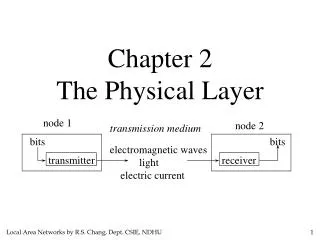
Chapter 2. The PHISICAL LAYER. 고려대학교 네트워크 연구실. The Telephone System. PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network Structure of the telephone System Fully interconnected network Centralized network Two level hierarchy See Fig. 2-14. Major Components. Local loop

Chapter 2. The PHISICAL LAYER
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 2. The PHISICAL LAYER • 고려대학교 • 네트워크 연구실
The Telephone System • PSTN • Public Switched Telephone Network • Structure of the telephone System • Fully interconnected network • Centralized network • Two level hierarchy • See Fig. 2-14
Major Components • Local loop • Twisted pairs, analog signaling • Trunks • Fiber optical, mostly digital • Switching Office Intermediate Switching office Toll office Toll office End office End office Toll connecting trunk Very high bandwidth Intertoll trunks Toll connecting trunk Local loop Local loop
The Local Loop • Advantage of Digital • Attenuation 과 Distortion에 강함 • 음성이나 데이터 이미지 등을 산제 시켜 circuit과 equipment의 사용을 효율적으로 만들 수 있다. • 전송비용이 싸다. • 좀더 쉽다.
The Local Loop • Long distance trunk는 요즘들에 digital로 많이 바꾸었으나 local loop의 경우 비용 문제 때문에 아직도 analog를 쓴다 • Computer는 digital Data를 전화선을 통해 보내길 원하나 local loop은 analog이기 때문에 modem과 codec이 필요하다.
Transmission Impairment • Attenuation • The signal falls off logarithmically with the distance • Frequency dependant • Delay distortion • Frequency dependant • Noise
Modem • Modulation의 이유 • Attenuation과 Delay는 frequency에 의존적이다. • Rectangular has a wide spectrum, so strong attenuation and delay distortion. • 즉 DC signaling이 적합하지 않으므로 AC signaling을 쓴다.
Modem • Echo effect • Transmission line에서 주파수가 반사되는 현상. 즉 자신의 목소리가 자신에게 들리는 현상 • Count attack for echo effect • Echo suppressor : half-duplex • In-band signaling : detect pure tone at 2.1Khz • Echo cancelers
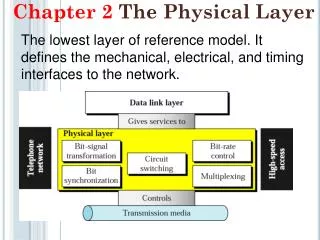
RS-232-C and RS-449 • The interface btw the computer or terminal and the modem is an example of a physical layer protocol • Physical layer standard • Specification -mechanical,electrical,functional,procedural see text p114 to p115
Multiplexing • 경제적인 이유로 Multiplexing이 선호됨. • Multiplexing 종류 • FDM(frequency division multiplexing) • WDM(Wavelength division multiplexing)For fiber optic channel, use Prism • TDM(time division multiplexing) • PCM(pulse code modulation),DM,etc • CDM(code division multiplexing)
SONET(Synchronous Optical Network • A standard of optical TDM system • Four Major Goal • Make it possible for different carriers to interwork • Unify the U.S.,European,Japanese digital systems • Multiplexing multiple digital channels together. • Provide support for OAM (operations,administration,maintenance)
SONET Source MUX Destination MUX • SONET Frame • 810 byte ( 90 columns, 9 rows ) • 125usec per byte, 51.84Mbps • See Fig 2-30 MUX Path Pepeater Line Pepeater Section Photonic Section Line Path
Switch • Crossbar Switches • The simplest kind • Use many line, multicasting enable • Space Division Switches • Time Division Switches • Time slots • Time slot interchange
ISDN( Integrated Services Digital Network ) • Narrowband ISDN( N-ISDN ) • Digital Bit Pipe • Conceptual pipe • Support multiple independent channels by time division multiplexing of the bit stream • 다수의 망 • 공통 신호망 • 회선 교환망 • 패킷 교환망
ISDN • N-ISDN • Channel type • 4kHz analog telephone channel • 64kbps digital PCM channel for voice or data • 8 or 16kbps digital channel • 16kbps channel for out-of-band signaling • 64kbps digital channel for internal ISDN signaling • 384,1536 or 1900kbps digital channel • Focus on64Kbps channel
ISDN • N-ISDN • 단점 • 대역폭 제한 • 실시간 서비스 어려움 • 너무 망이 많다. • 망관리 힘듦 • 서비스 채널 속도 고정
ISDN • Broadband ISDN AND ATM • 광대역 • 단일망 • 보통의 경우 Optical Fiber사용, 높은 안정성 • ATM 사용
ATM( Asynchronous Transfer Mode ) • 정의 • 53Kbytes ( 5:header, 48:Payload )의 cell를 ATDM(Asynchronous TDM)방식으로 전송시키는것 • ATDM: 정보 전송량에 따라 time slot의 길이가 동적 할당된다. • Asynchronous • 동일 channel상의 cell이 불규칙적으로발생 channel은 trunk의 입장에선 필요시에만 사용 • Transfer Mode • Transmission,Multiplexing,Switching
ATM • 장점 • 현제의 제공중인 서비스와 앞으로 요구될 서비스의 융통성 확보 • 동적 대역폭 할당 가능 • 전송하는 cell의 수를 변화 시킴 • QoS 제공,보장 • 모든 정보의 통합화 된 서비스 가능
ATM • Cell 전송 • Connect Oriented • But implemented internally with packet switching • Virtual circuit • Permanent Virtual circuit • Switched Virtual circuit
ATM Switches • General Model • Same number of input and output • Common goals of ATM switches • Switch all cells with as low a discard rate as possible • Never reorder the cells on a virtual circuit
ATM Switches • Problem • 같은 cycle에 다수의 일력이 같은 줄력 단으로 가길 바랄때. • 해결방법 • 출력단에 버퍼링 • 대표적인 종류 • The Knockout Switches • Buffering하는 수를 줄이자. • The Batcher-Banyan Switch
CELLUALR RADIO • Paging System • Analog System • Cordless system: CT-1,CT-2,CT-3(roaming) • Analog Cellular Telephone • AMPS( Advanced Mobile Phone Service) • Digital System • PCS (Personal Communication Service) • IMT-2000 ( FPLMS ) • Satellites Communication ( LEO )
CELLUALR RADIO • Cellular • Frequency or Channel Reuse • Channels ( AMPS case ) • CC: manage the system • PC: alert mobile users to calls for them • AC: call setup and channel assignment • DC: for voice,fax or data • CC.PC: downlink • AC,DC: bidirectional