Light as a Wave
300 likes | 653 Vues
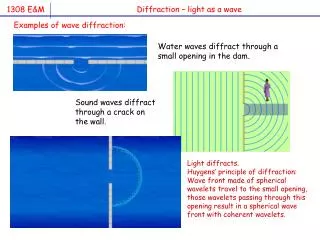
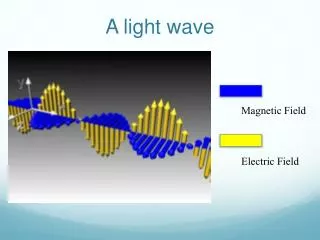
Light as a Wave. One way to think about light is as a traveling wave A wave is just a disturbance or vibration in some medium ( water, air, space) A wave travels through a medium but does not transport material A wave can carry both energy and information. Wave Terminology. Wavelength λ

Light as a Wave
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Light as a Wave • One way to think about light is as a traveling wave • A wave is just a disturbance or vibration in some medium • (water, air, space) • A wave travels through a medium but does not transport material • A wave can carry both energy and information
Wave Terminology • Wavelengthλ • distance between two similar points on the wave • Measured in meters • Amplitude • the height of the wave compared to undisturbed state • Frequency • the number of waves passing in a given amount of time • Measured in Hertz (Hz) –cycles per second
Wave Relationships • We can relate the properties of a wave to one another • = Velocity or speed of light (c) 3.0x108 m/s is a constant for all EM Radiation • = Wavelength measured in meters (m) • = Frequency measured in Hertz (Hz)
Practice • What is the wavelength of radiation with a frequency of 1.50 x1013 Hz? • What frequency is radiation with a wavelength of 5.00 x 10-6 cm?
Light as a Particle • 17th century Isaac Newon proposes that light is made up of small discrete particles called “corpuscles” which travel in straight line with a finite velocity and possess kinetic energy. • Albert Einstein returned to the idea that light existed as particles. He proposed that light could be described as quanta of energy that behave as if they were particles. Light quanta are called photons. • explain the photoelectric effect
Photoelectric Effect • When light shines on metals, electrons are ejected from their surface. • A certain frequency has to be achieved or the effect does not work Red light will not cause electrons to eject!
Photoelectric Effect in action Practical applications in photoelectrical cells used for solar cells, and solar powered calculators.
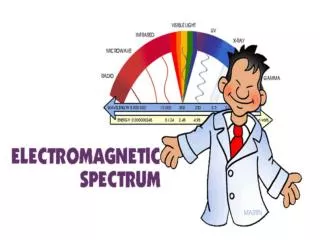
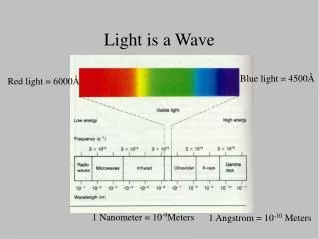
The Electromagnetic Spectrum • Human eyes are only able to process information from the visible part of the spectrum • Toward longer wavelengths, the spectrum includes infrared light, microwaves, and radio • Toward shorter wavelengths, the spectrum includes ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays • All of these are forms of electromagnetic radiation
Radio waves • Longest wavelength EM spectrum • Uses: • TV broadcasting • AM and FM broadcast radio • Avalanche beacons • Heart rate monitors • Cell phone communication
Microwaves • Wavelengths from 1 mm- 1 m • Uses: • Microwave ovens • Bluetooth headsets • Broadband Wireless Internet • Radar • GPS
Infrared Radiation • Wavelengths in between microwaves and visible light • Uses: • Night vision goggles • Remote controls • Heat-seeking missiles
Visible light • Only type of EM wave able to be detected by the human eye • What we see as white light is actually made up of a continuum of components • Traditionally, we break white light into red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet (ROY G BIV) • There is actually a continuous transition of color, each with its own wavelength and frequency
Ultraviolet • Shorter wavelengths than visible light • Uses: • Vitamin D • Black lights • Laundry additive – bright whites • Sterilizing medical equipment • Water disinfection • Security images on money
X-rays • Tiny wavelength, high energy waves • Uses: • Medical imaging • Cancer treatment • Airport security • Inspecting industrial welds
Gamma Rays • Emitted from atoms in radioactive decay Cobalt 60 & cosmic radiation • Smallest wavelengths, highest energy EM waves • Uses • Food irradiation • Cancer treatment • Sterilization of Equipment • Treating wood flooring
Why are so many emergency trucks & signs YELLOW/GREEN The radiation to which our eyes are most sensitive has a wavelength near 550 nm in the yellow-green region of the spectrum.
EM Spectrum in Astronomy • If we could only observe in visible light, our knowledge of the universe would be greatly limited • By looking at objects at different parts of the EM Spectrum, we get a different view and lots more information Jupiter seen at different wavelengths of light
The Sun at Different Wavelengths Visible Ultraviolet X-ray X-ray