Unit 10 Strong Forms & Weak Forms
180 likes | 840 Vues
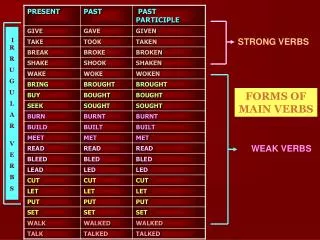
Unit 10 Strong Forms & Weak Forms. Strong forms & Weak forms. Strong forms: stressed forms Weak forms: unstressed forms (/ /),e.g. Words Strong Vowels Weak Vowels at / / / / has // //

Unit 10 Strong Forms & Weak Forms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Strong forms & Weak forms • Strong forms: stressed forms • Weak forms: unstressed forms (//),e.g. Words Strong Vowels Weak Vowels at // // has // // she /:/ // could // //
Some English words only have strong forms, but other • words have both strong forms and weak forms. These words are called structural words. They include many thousands in English , but among them 45 are important to English learners, including the following 5 groups : • 1)determiners 2)pronouns ; 3)connectives ; • 4)auxiliary verbs; 5) prepositions. • 1.The factors that influence the usage of strong form or • weak form of a structural word : • 1) the position of a word in a sentence; • 2) the degree of stress of a word ; and • 3) other factors . • When they bear stress , no change in sound quality • takes place and so the strong forms are • used . Otherwise, weak forms are used.
2. Signs which a weak form of a word may be noted by: • (1) a shortening in the length of a vowel,e.g. • /i:/------/i/ as in we, he , been. • /u:/ -----/u/ as in to, who, you. • /[:/-----/[/ as in sir, were, per. • (2)a change in a vowel sound, e.g. • was /wCz/ ------ /w[z/ , • us /Qs/----- /[s/, • by /bai/------- /b[, bi/. • (3) the absence of a sound, e.g. • and/And/-------/nd,[n,n/ , • them/Tem/-------/Tm/, • her/hE:/-------/[:,[/.
3. The rules for the uses of strong forms: 1) Strong forms are used when structural words occur at the end of a sense group or a sentence. e.g. • Music is what I fond of ./ What are you looking at ? • What is he waiting for ?/ Where did you get from ? 2) Strong forms are used when such words are in contrast. e.g. • I have a letter for him ,not from him. 3) Strong forms are used when such words are used for emphasis. • I think maybe ``you know it . 4) Strong forms are used when they are being used as nouns. e.g. • Did you say ``“he”? • “A”, “an ”,and “the” are articles. • Note : Negative contract forms do not take weak forms, such as haven’t, can’t, etc