Understanding Buffer Overflow: A Simple Program Exploit Explained
160 likes | 301 Vues
This guide explores the concept of buffer overflow through a simple program example. Our goal is to demonstrate how malicious code can exploit vulnerabilities in a program using a buffer overflow attack. We analyze the stack before and after the critical function calls, revealing how return addresses can be overwritten by input that exceeds buffer size. Additionally, we discuss the internal aspects of the stack, potential consequences of such attacks, and practical advice on avoiding insecure functions. Learn how to identify and safeguard against these vulnerabilities.

Understanding Buffer Overflow: A Simple Program Exploit Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Buffer Overflow – A simple program • Our goal is to execute the hack() function Could be worst!
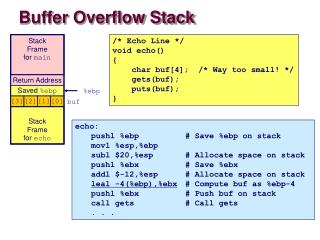
Buffer Overflow – Internal aspects of the program Stack before the scanf call Stack after the scanf call print_it() and hack() functions addresses
Buffer Overflow – Running the program The code of ‘A’ is 0x41!
Buffer Overflow – The x86 stack Ends of the stack Call parameters Stack Frame (Of who calls the subroutine) Return Address %EBP register Preserve original register values Stack Frame (currently) Make space for local variables in subroutines %ESP Stack Pointer (32 bits)
Buffer Overflow – The attack Ends of the stack Call parameters Stack Frame (Of who calls the subroutine) Write chars until change the return address Return Address %EBP register Preserve original register values Stack Frame (currently) Make space for local variables in subroutines Buffer s stays here
Buffer Overflow – Running once more We want to put this address here
Buffer Overflow – The attack It’s used a String larger than s buffer is expecting and that stays over the return value The return address was changed Mallicious code
Buffer Overflow – But where came from the hack() function?? Usually buffers don’t have enought space to store all the code that is going to be executed (i.e. s[] buffer does not have enought space to the binary code of hack()), so we only need to make the program to read data from someplace, and store it in a way that is possible to locate it later. In this case is just necessary to make the returning address point to the right location (e.g., a image!)
Buffer Overflow – But... • Hackers could not have access to the source code to discover the buffer sizes... It’s very easy to incrementally enlarge the input data until a crash occur. This way, the buffer size is discovered.
Buffer Overflow – The correct code Don’t use “insecure functions”, or when it’s absolutely necessary to use them special cares are needed. E.g., gets()/fgets() scanf()/fscanf() strcat()/strcpy() ...
Credits... The original (and Portuguese) version of these presentation belongs to Professor Paulo Marques Paulo Marques Departamento de Eng. Informática Universidade de Coimbra pmarques@dei.uc.pt