Internet History - Japan
130 likes | 374 Vues
Draft. Internet History - Japan. Aug. 28, 2003 Kazunori Konishi. Objectives. (1) Recording of the Pioneers’ efforts (2) Study on technical trend for investing the resources.

Internet History - Japan
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Draft Internet History - Japan Aug. 28, 2003 Kazunori Konishi 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
Objectives (1) Recording of the Pioneers’ efforts (2) Study on technical trend for investing the resources. (3) Lessons Learned from the History for the new problems; human nature will not change, though political or technical environments might face the big changes. =>> “Grass roots activities” should be based on human nature; ex. AP* activities. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
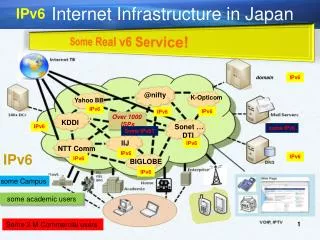
Big Picture in Japan 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
History of International Networks 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
ALOHAnet(1980) • Lead by Professor Norman Abramson @ U-Hawaii : origin of Ethernet • Coordinated at Pacific Telecom- munications Council(PTC) • Professor Oizumi @ Tohoku-U joined the network. • NASA(KDD) donated the satellite circuit, recommended by MPT • KDD was rich, with the monopoly & high cost of the services. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
UUCPnet/Usenet(1985) • Operated by KDD Labs. on a volunteer basis. • PSTN & PSDN were used. • The partners became commercialized later on: UUnet, Eunet. • “Membership” allowed the operation over the public networks, without any license. • Limited resources were allocated, because OSI was promising in those days. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
BITNET(1985) • IBM donated the circuit & equipments, promoting SNA. • Science University of Tokyo(SUT) organized private universities. • The US power enabled to use the leased circuit without any license. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
WIDE(1989) • Jun Murai organized the large number of engineers at commercial companies & universities. (Murai had organized UUCP domestic network “JUNET”) • U-Hawaii’s PACCOM project organized AP regional networks. • Governments were still persistent in OSI, though they knew OSI was being defeated. (US Gov. also declared the adoption of OSI products) • Industries & Universities required the “illegal?” activities of WIDE. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
SINET(1992) • Government was forced to adopt TCP/IP in addition to OSI. • OSI was the primary protocol for a while. • The big budget enabled the large membership. • A Ministry can use the leased circuit without any license; not hierarchy among governments. • Government is not so flexible. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
AI3 Network (1995) 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
APAN(1998) • NSF required the transit services over TransPAC link. • The owners of point-to-point links started the collaborated operations. • AP Regional networks were developed with a hub in Tokyo. • The institutions with advanced research projects are allowed to use TransPAC link. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
Over Provisioning of the bandwidth Demand in Asia is roughly 10 Gbps now. Issue: How can we bridge the gap? Healthy business of telecom carriers should be protected. 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting
Number of RFCs by Japanese 2003 Busan AP*Retreat Meeting

















![Internet Applications [History]](https://cdn3.slideserve.com/6788660/internet-applications-history-dt.jpg)

