Content based Image Retrieval using Interest Points and Texture Features
10 likes | 163 Vues
This study explores an efficient method for content-based image retrieval utilizing interest points and texture features, specifically through local Gabor features. The representation of images leverages both feature vectors and histogram sets created from interest point detections. Utilizing a nearest neighbour search approach, we evaluate image similarity based on the amplitude distributions of local features. Our algorithms were tested on databases containing diverse images, yielding promising precision rates in retrieval accuracy. Discover the full methodology and performance results in our demo.

Content based Image Retrieval using Interest Points and Texture Features
E N D
Presentation Transcript
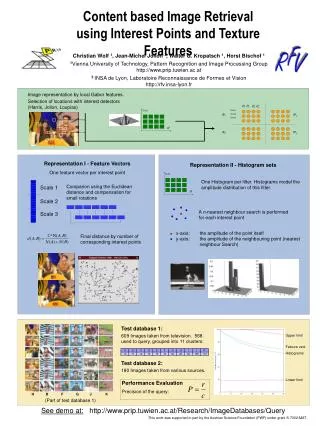
Scale Scale Scale 1 Scale 2 Scale 3 x-axis: the amplitude of the point itself y-axis: the amplitude of the neighbouring point (nearest neighbour Search) Content based Image Retrieval using Interest Points and Texture Features Christian Wolf 1, Jean-Michel Jolion 2, Walter G. Kropatsch 1, Horst Bischof 1 1Vienna University of Technology, Pattern Recognition and Image Processing Group http://www.prip.tuwien.ac.at 2 INSA de Lyon, Laboratoire Reconnaissance de Formes et Vision http://rfv.insa-lyon.fr Image representation by local Gabor features. Selection of locations with interest detectors (Harris, Jolion, Loupias) Scale 1 Scale 2 Scale 3 IP1 IP2 IP3 IP4 Representation I - Feature Vectors One feature vector per interest point Representation II - Histogram sets One Histogram per filter. Histograms model the amplitude distribution of this filter. Comparion using the Euclidean distance and compensation for small rotations A n-nearest neighbour search is performed for each interest point Final distance by number of corresponding interest points Test database 1: 609 Images taken from television. 568 used to query, grouped into 11 clusters: Upper limit Feature vect. Histograms Test database 2: 180 Images taken from various sources. Lower limit Performance Evaluation Precision of the query: H B F G J K (Part of test database 1) See demo at: http://www.prip.tuwien.ac.at/Research/ImageDatabases/Query This work was supported in part by the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF) under grant S-7002-MAT