Property Tax Administration
240 likes | 376 Vues
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of property tax calculations within various districts, including fire, school, and waste management districts. It covers essential concepts such as tax base computation, budget setting, intergovernmental aid subtraction, and the calculation of mill rates. The document explains the difference between statutory and effective property tax rates, assessment methods, and the implications of rate-based and levy-based systems. Additionally, it addresses thought-provoking questions related to changing property values and their effects on tax obligations.

Property Tax Administration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tax Districts District Tax Calculation Assessment Calculation of Tax Obligations Property Tax Administration
Waste Management Districts
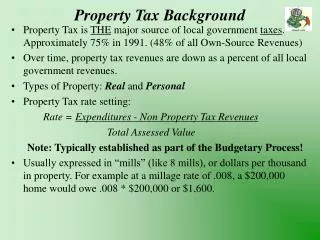
District Tax Levy • Compute tax base (add up the assessed values of all the taxable real property in the district = $100 million). • Set the budget ($2.5 million) • Subtract intergovernmental aid ($1M) • Divide the remainder ($1.5 million) by the tax base ($100 million) to calculate the statutory property tax rate = .015 or 1.5 percent or 15 mills
Mill Levy Property tax rate. A mill is equal to $1.00 of tax for each $1,000 of assessment, or .1 percent. To calculate the property tax multiply the assessment of the property by the mill rate and then divide by 1,000. For example, a property with an statutory assessed value of $500,000 located in a municipality with a mill rate of 10 mills would have a property tax bill of $5,000.00 per year
Rate Based Systems • Specify a Mill Rate (or Percentage Tax Rate) • Apply to tax base • Fit budget to anticipated revenues • Propose a change in tax rate consistent with spending plans
Rate Based Systems • Specify a Mill Rate (or Percentage Tax Rate, e.g., 15 or 1.5%) • Apply to tax base • Fit budget to anticipated revenues • Propose a change in tax rate consistent with spending plans
Rate Based Systems • Specify a Mill Rate (or Percentage Tax Rate, e.g., 15 or 1.5%) • Apply to tax base ($100M = $1.5M) • Fit budget to anticipated revenues • Propose a change in tax rate consistent with spending plans
Rate Based Systems • Specify a Mill Rate (or Percentage Tax Rate, e.g., 15 or 1.5%) • Apply to tax base ($100M = $1.5M) • Fit budget to anticipated revenues ($2.5M = $1M + $1.5M) • Propose a change in tax rate consistent with spending plans
Rate Based Systems • Specify a Mill Rate (or Percentage Tax Rate, e.g., 15 or 1.5%) • Apply to tax base ($100M = $1.5M) • Fit budget to anticipated revenues ($2.5M = $1M + $1.5M) • Propose a change in tax rate consistent with spending plans (if necessary)
Assessment • True market value • Method of comparables • Econometric (hedonic pricing) assessment* • Book (acquisition cost minus depreciation), replacement cost, cash flows Residential Real Estate Commercial Real Estate *Accuracy is a function of frequency
Proportional Assessment • Usually expressed as as proportion of market value • Often used to discriminate in favor of certain property types • Other statutory standards Oregon = AV 1994 plus 3% Per annum = 1.65(AV 1994), or MV, whichever is less, in FY2011
Statutory vs Effective Property Tax rates • Property tax bill is calculated by multiplying the sum of tax rates that apply to the property by the property’s AV. • The effective tax rate is found by dividing the tax bill by MV
Statutory vs Effective Property Tax rates • Property tax bill is calculated by multiplying the sum of tax rates that apply to the property by the property’s AV. • The effective tax rate is found by dividing the tax bill by MV (a better measure might take account of the MV of all the property in a jurisdiction and not just the taxable property).
Thought Questions • In a levy-based system, what happens to tax rates if you add to the tax base? To a district’s revenues? What happens to your tax bill if your neighbor’s property increases in value and yours doesn’t? • In a rate-based system, what happens to tax rates if you add to the tax base? To a district’s revenues? What happens to your tax bill if your neighbor’s property increases in value and yours doesn’t?