Exploring Social Anxiety: Cultural Expectations and Epigenetic Influences
80 likes | 200 Vues
This presentation delves into the prevalence of social anxiety, examining the mismatch between cultural social expectations and individual perceptions. We will explore the hypothesis that increased distance between these factors leads to higher levels of social anxiety. A psychometric instrument will be introduced to measure cultural/social expectations and personal perceptions, alongside self-reported anxiety levels. This research is grounded in evolutionary anthropology and gene-culture co-evolution, hinting at the profound implications for understanding social behavior across human groups.

Exploring Social Anxiety: Cultural Expectations and Epigenetic Influences
E N D
Presentation Transcript
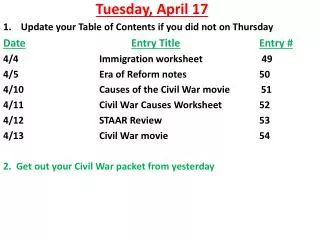
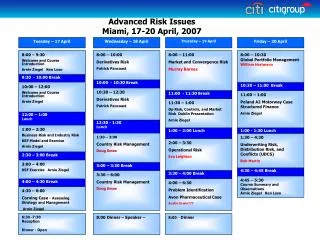
ASM 300 APRIL 17 1:30 – 1:45 * Announcement – answers to questions on Zak’s paper, the groups that did not finish will share – Tuesday of next week at the beginning of class * A preliminary outline of a ‘What Did We Learn’ presentation 1:45-2:20 Dr. Hill, the Trust Game exercise 2:20 Don Johanson
Why is social anxiety more prevalent than any other psychological ailment in all human groups? The big research question
Deductive conceptual framework The human brain is designed to be ‘co-opted’ by culture and biology (conclusion based on theoretical and empirical research on gene-culture co-evolution and evolutionary anthropology) If this is true, then I would expect to find that social anxiety is driven by a mismatch at the level of the individual between cultural social expectations and epigenetically determined perceptions of the social self.
Hypothesis As the ‘distance’ increases between cultural social expectations and epigenetically determined perceptions of the social self, levels of social anxiety will also increase.
Predictor and outcome variables Predictor variable – ‘distance’ is measured using a psychometric instrument for assessing cultural/social expectations (CSE) and epigenetically determined perceptions of the social self (ESS). Example: (CSE) How perfectly articulate are you expected to be when you describe your feelings/ideas in “___X____” social context? (scale 1-5, from least articulate to most articulate) (ESB) In “___X____” social context, how would you rate your ability to be articulate? (scale 1-5; from least articulate to most articulate) Outcome variable – measured in units of self-reported social anxiety’ using a psychometric instrument Example: On a scale from lowest to highest, how anxious do you feel after presenting a speech in x social and cultural context (scale: 1 – not anxious at all; 5 – extremely anxious)
To be continued.. • Research design • Retrospective longitudinal with cross sectional components • Number of subjects • Inclusion criteria for subjects
To be continued.. • Expected implications of the findings (i.e., anthropological significance)