Channel Rejection in Receivers
40 likes | 292 Vues
Learn about channel rejection in receivers, measuring interference handling, and signal power dynamics. Explore examples and sensitivities for WLAN chips.A receiver's capability to reject unwanted signals from adjacent or co-channel sources is essential for optimal performance in modern communication systems. This title provides insights into key metrics and scenarios, helping to understand receiver behavior.

Channel Rejection in Receivers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
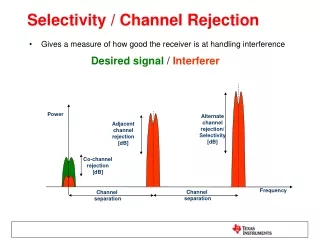
Selectivity / Channel Rejection • Gives a measure of how good the receiver is at handling interference Desired signal / Interferer Power Alternate channel rejection/ Selectivity [dB] Adjacent channel rejection [dB] Co-channel rejection [dB] Frequency Channel separation Channel separation
Blocking Desired signal / Interferer Power Frequency Frequency Offset • Gives a measure of how good the receiver is at handling interference from a source further away in frequency
Receiver Example Desired signal / WLAN Power Frequency 5 MHz Chip A Chip B Sensitivity: -100 dbm -97 dBm Blocking: 27 dB +/- 5 MHz offset 55 dB +/- 5 MHz offset Case 1: The power from the WLAN is –80 dBm. Receiver A can receive a –100 dBm signal. Receiver B can receive a –97 dBm signal. No degradation in receiver sensitivity.
Receiver Example 2 Desired signal / WLAN Power Frequency 5 MHz Chip A Chip B Sensitivity: -100 dbm -97 dBm Blocking: 27 dB +/- 5 MHz offset 55 dB +/- 5 MHz offset Case 2: The power from the WLAN is –40 dBm. Receiver A can receive a -40-27 = -67 dBm signal. Receiver B can receive a -40-55 = -95 dBm signal. Receiver B have 27 dB better receiver sensitivity.