Transposable Elements
800 likes | 4.25k Vues
Transposable Elements. DNA Sequences That Change Positions in the Genome. Types of Transposable Elements. Transposition: movement of a transposable element. Characteristics of Transposable Elements.

Transposable Elements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Transposable Elements DNA Sequences That Change Positions in the Genome
Types of Transposable Elements Transposition: movement of a transposable element
Characteristics of Transposable Elements • All elements have direct repeats: short repeated sequences flanking the element, arise by transposition
Characteristics of Transposable Elements • Some elements have terminal inverted repeats
Characteristics of Transposable Elements • Carry gene for enzyme that catalyzes transposition • transposase for elements that use a DNA intermediate • reverse transcriptase for elements that use an RNA intermediate • May contain other genes
Mechanisms of Transposition • Use of a DNA Intermediate • Replicative- new copy in new location, old copy retained at original site, element is used as template to produce the new copy
Mechanisms of Transposition • Use of a DNA Intermediate • Non-replicative: moves to another site without replication of the element
Mechanisms of Transposition • Use of an RNA Intermediate • element is transcribed • reverse transcriptase produces a double-stranded DNA copy for insertion at another site
Types of Retrotransposons • Viral Retrotransposons • resemble retroviruses = viruses with an RNA genome • Long terminal direct repeat at each end • Carry genes for enzymes usually found in RNA viruses
Types of Retrotransposons • Non-viral Retrotransposons • do not resemble retroviruses • two types in humans • LINES = long interspersed elements • 6-7 kb long • example: L1 has 600,000 copies, represents 15% of human DNA • SINES = short interspersed elements • 300 bp long • example: Alu has 1 million copies, represents 10% of human DNA
Applying Your Knowledge • Retrotransposon • Transposon • Both retrotransposons and transposons • Neither retrotransposons nor transposons • Which type of transposable element • Uses a DNA intermediate for transposition? • Contains long terminal repeats on its ends? • Generates direct repeats as a result of transposition? • Carries a gene for reverse transcriptase? • Can insert a copy in a new location while leaving the old copy at the original site?
Effects of Transposition Transposable elements can: • Cause mutations in adjacent genes • Cause chromosomal rearrangements • Relocate genes
Possible Advantages of Transposable Elements Transposable elements may: • Create genetic diversity • Act as promoters • Allow recombination between plasmid and genomic DNA when multiple copies of the element are present • Carry antibiotic resistance genes, conferring an advantage on bacterial cells • Increase the number of copies of an exon or gene
Examples of Transposable Elements • Bacterial Insertion Sequences and more Complex Transposons • Ac-Ds Elements in Corn • P elements in Fruit Flies
Insertion Sequences contain only the elements needed for transposition Composite Transposons contain DNA that has insertion sequences on both sides Transposable Elements in Bacteria Antibiotic resistance genes are often included
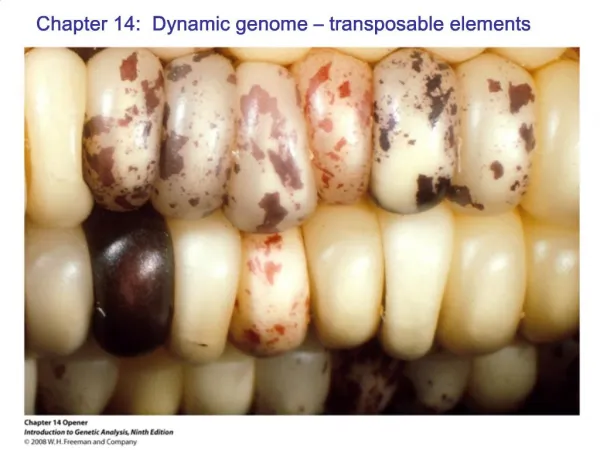
Ac and Ds Elements in Corn • Ac stands for activator element • Ds stands for dissociative element • Barbara McClintock showed that --transposition of the Ds element altered kernel coloration --movement of the Ds element required the activity of Ac element Animation available at http://www.dnalc.org
Transposition of Ds Element Disrupts Gene Controlling Kernel Color
Relatedness of Ac and Ds Elements For transposition, Ds elements require the transposase produced by the Ac element.
The P Element in Drosophila Codes for a Transposase and a Repressor of Transposition No repressor Repressor produced P element inserts in multiple locations Transposition is repressed
P element codes for transposase P element with gene of interest can insert into chromosomeswith help of plasmid containing only transposase. Use of the P Element As a Vector in Drosophila
Applying Your Knowledge • Ac-Ds Elements • Alu Element • Insertion Sequence • P element • Which type of transposable element • Contains only the sequences needed for transposition in bacteria? • Represents a SINE found in humans? • Is used to insert genes into fruit fly chromosomes? • Causes reversible alterations for kernel color in corn?