A Secure JBoss Platform
240 likes | 466 Vues
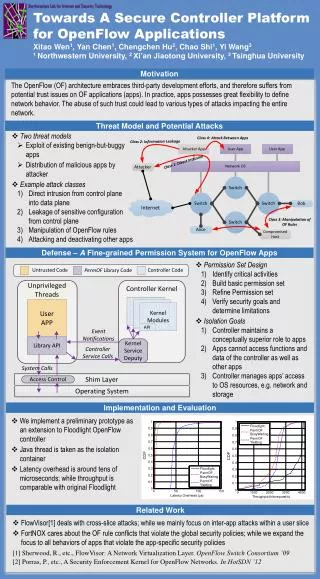
A Secure JBoss Platform. Nicola Mezzetti Acknowledgments: F. Panzieri. Outline. Scenario JBoss Invocation Mechanism JBoss Security J2EE Security (JAAS based) JBoss Custom Security (Security Proxy) Using RMI over SSL in JBoss Conclusions References. Application. Inter-Org.

A Secure JBoss Platform
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A Secure JBoss Platform Nicola Mezzetti Acknowledgments: F. Panzieri
Outline • Scenario • JBoss Invocation Mechanism • JBoss Security • J2EE Security (JAAS based) • JBoss Custom Security (Security Proxy) • Using RMI over SSL in JBoss • Conclusions • References TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Application Inter-Org. Interaction Regulation QoS Monitoring + Violation Detection QoS Manag. + Monit. + Adapt. QoS Enabled Application Server Trusted Transport Layer Presentation Scenario TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Invocation Mechanism • Key Abstractions: • Invocation: actual call made by the client • Dynamic Proxy • From client it is seen to implement the interfaces it offers; • Invocation Handler (IH): • Processes invocations on behalf of the dynamic proxy • Interceptor: • Implements a behaviour specific for a given service; • Invoker: Carry the invocations in JMX target node • masks phisical details to the client proxies TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Invocation Dynamic Proxy Invoke(A,p[ ]) Method A(p[ ]) Invoker Invocation Handler Typed Interface Interceptors JBoss Invocation Mechanism:the Client Side TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Interceptors • Implement transparency • Each service the EJB relies may have an associated interceptor to enrich IPCs instances with specific meta-information • e.g., Security Interceptor adds principal name and credential • They are MBeans as well • InterceptorProxy at client side, Interceptor at server side TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Invokers • IPC Transparency • Each transport protocol has its specific invoker • Invokers are the actual IPC endpoints • JBoss provides JRMP, HTTP and IIOP • JBoss allows the integration with custom Invokers • They are MBeans as well • InvokerProxy at client side, Invoker at server side TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Interceptors Invocation EJB Instance Remote Invoker JMXMicrokernel EJB Container JBoss Invocation Mechanism:the Server Side I The Remote Invoker is directly connected to the EJB Container; the invoker lets the microkernel route the invocation. TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Invocation Mechanism:the Server Side II • The RemoteInvoker captures the invocation and passes it to the container • RemoteInvoker enables remote invocations • The invocation is passed to the container through the JMX server • The invocation passes through the invocation handler that captures information added at client side for enabling the services TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Security • In JBoss, the EJB security layer extends the Interceptor Abstraction supporting • J2EE declarative security model (RBAC) • JAAS based • custom security via SecurityProxy architecture • Designed for enabling application specific security TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JAAS declarative security • JAAS Abstractions: • Subject: The abstraction of an individual • Collection of principals and credentials (public and private); • Principal: A unique identifier of an individual within a specific application; • Credential: Object bound to a specific principal that is used to carry out authentication; • Role: A name that qualifies the permissions of a principal within an application. TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Access Control:Client Authentication and Role Assignment • Authentication steps: • SecurityInterceptor encapsulate principal and credential into the invocation; • At server side, principal and credential are checked • Authentication creates Subject with PrincipalsSet containing: • One or more principals • A group of role names from the application domain • An optional group corresponding to the caller principal TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
RMI MBean Client Authorization Login “Nicola” mzzncl Authentication happens at server side: - In standard JBoss passwords are trasmitted in clear - JBoss is independent from authentication technologies TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Authentication • By default JBoss maintains a password based authentication mechanism • Custom authentication infrastruction can be integrated by implementing: • Callback • CallbackHandler • Configuration • LoginContext • LoginModule • An implementation of Secure Remote Password protocol is included TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Access Control:Role Membership Check • Authorizing access to an EJB home or remote interface method consists of: • Obtaining the names of the roles allowed to invoke the method (from the Deployment Descriptor) and… • Invoking doesUserHaveRole(Principal,Set) from RealmMapping interface • If the RealmMapping grants the Principal with at least one of the roles in Set, then the access to the method is granted. TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Access Control:SecurityDomain • SecurityDomain: • Application wide security manager • Extends SecurityManager and RealmMapping • It is responsible for implementing both principal authentication and authorization • Base for a multi-domain security architecture to support ASPs TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Access Control:SecurityManager and RealmMapping • SecurityManager • Validates credentials associated with principals • RealmMapping • Responsible for principals and role mapping • Validates the roles to which an environment principal belongs • Validates a principal to belong to a role TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
JBoss Access Control:SecurityProxy • SecurityProxy: • Designed to Implement application specific policies; • Additional authorization is performed after any declarative authorization checks (enfoced by SecurityDomain); • Invocation parameters are passed to the security proxy via • invokeHome(method, args[]) • invoke(method, args[]) • SecurityProxy can reject access by throwing a SecurityException TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Considerations on JBoss Security • RMI technologies do not provide us with security guarantees • It does not protect against replay attacks • Configuration is complex and timely-expensive • If application security is not properly configured, different applications can interfere with each other • e.g., an EJB could illegitimately invoke another EJB’s operation • configuration is considerably time consuming (compared with application development time) TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Secure Socket Layer • SSL technology provides • Authentication: SSL handshake • Both the communicating parties trust the identity of each other • Secrecy: Shared key • Shared session key efficiently provides secrecy • Integrity: Message Authentication Code (MAC) • MAC enables to identify message changes in transit TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Using RMI over SSL in JBoss • SecurityDomain interface provides operations for supporting secure transport layers • Customizable keyStore, KeyManagementFactory and TrustManagementFactory • JBoss comes with an SSL implementation of • RMIClientSocketFactory • RMIServerSocketFactory • An EJB Invoker for RMI over SSL Socket has to be implemented TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Future Work I • We are going to • evaluate JBoss with • Secure Socket Layer • assess the RMI over SSL within JBoss performance loss by using ECperf • And compare it with standard JBoss performances • If loss is considerable, a solution based on SRP and adequate role configuration could provide a good security tradeoff TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004
Concluding Remarks • JBoss enables the integration with custom security mechanisms at different logical layers • SecurityProxy and Interceptors for masking application dependent techniques • Invokers for transport layer techniques • RMI over SSL is to be tested for understanding how much inter-EJB authentication affects JBoss platform performances TAPAS 5th Plenary Workshop - Bologna, 19-20 February 2004