HIV/AIDs Education
120 likes | 438 Vues
HIV/AIDs Education. California State University, Monterey Bay Case Study #2 February 12, 2014 Jonathan Borbon, Heidi Castro, Mireya Hernandez, Stephanie Solorio.

HIV/AIDs Education
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HIV/AIDs Education California State University, Monterey Bay Case Study #2 February 12, 2014 Jonathan Borbon, Heidi Castro, Mireya Hernandez, Stephanie Solorio
With the increase of HIV/AIDs, it is necessary for communities to be open to understanding the severity of this pandemic. Regardless of race, gender, class, religion, sexual orientation, disability, or any other aspects of what we look like or where we come from, HIV/AIDs affects all. HIV/AIDs Prevention Education: Recognizing the need for informing U.S. communities
Causes • Primary cause: Ignorance of people not being educated enough about HIV • Who to blame: Stigma • Indirect factors: • - Only gays get HIV • - Living with HIV; you will die • - View HIV as a threat • - Religious Views • “ Casual Theory” : Inadvertent Cause-Ignorance
Casual Story • In 2012, Only 21 States and DC; No mandate • -If taught voluntarily, must stress abstinence • (Advocates for Youth) • Resources AIDs.gov, CDC, ACA • Advocates for Youth and National Resource Center for • HIV/AIDS Prevention among Adolescents • Ryan White
Interest:Primary Stakeholders • HIV/AIDs Victims • U.S. Communities • Uneducated & Unaware
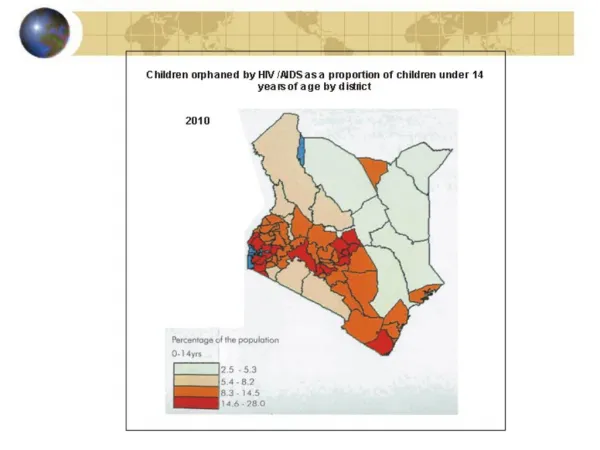
Why? & How? • 1 in 4 • Stigma & Abuse • United States Statistics • Informed & Aware 1 in 6
Secondary stakeholders • Secondary Stakeholders: Family Members & Friends, Clinics, Care providers • Parents of children, private school students, and public schools, Community members whom aren't affected directly by the infection • Both Primary & Secondary Stakeholders are mobilized for action • Examples: HIV testing on campus, propaganda, HIV marathons, fundraisers, etc
Summary • In progress :D
References Advocates for Youth. (n.d.). The Truth About Abstinence-Only Programs. Retrieved February 10, 2014, from Advocates for Youth: http://advocatesforyouth.org/publications/409 AIDS.gov. (n.d.). AIDS.gov Mission and Team. Retrieved February 10, 2014, from AIDS.gov: http://aids.gov/about-us/ CDC. Estimated HIV incidence in the United States, 2007–2010. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2012;17(No. 4). Published December 2012. CDC. Monitoring selected national HIV prevention and care objectives by using HIV surveillance data—United States and 6 U.S. dependent areas—2011. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report 2013;18(No. 5). Published October 2013. Mahon, N. (2012, June 06). Retrieved from http://aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/hiv-aids-101/statistics/ National Resource Center for HIV/AIDS Prevention among Adolescents. (n.d.). About the Resource Center. Retrieved February 9, 2014, from National Resource Center for HIV/AIDS Prevention among Adolescents: https://preventyouthhiv.org/content/about-us The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. (2012, June 1). State Sex and HIV Education Policy. Retrieved February 9, 2014, from kff.org: http://kff.org/hivaids/state-indicator/sexhiv-education-policy/ WHO.(2014). Retrieved from http://www.who.int/hiv/topics/vct/toolkit/components/policy/introduction/en/index2.html