Understanding Prokaryotes: Eubacteria and Archaea's Role in Life on Earth
120 likes | 261 Vues
Prokaryotes, primarily Eubacteria and Archaea, have existed for over 3.5 billion years and dominate life on Earth, inhabiting every hospitable environment and significantly outnumbering all animal life. They play crucial roles in ecosystems, including energy production and nutrient cycling. With over 10,000 known species, they exhibit diverse shapes and metabolic strategies. Bacteria reproduce rapidly through binary fission, and horizontal gene transfer enhances their genetic diversity. While some bacteria are beneficial, others pose health risks as pathogens. This overview highlights their importance and evolution.

Understanding Prokaryotes: Eubacteria and Archaea's Role in Life on Earth
E N D
Presentation Transcript
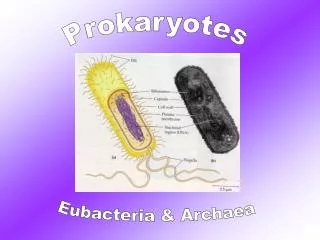
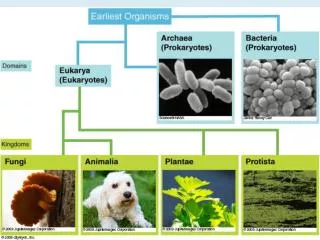
Prokaryotes Eubacteria & Archaea
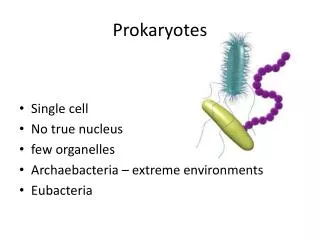
3.5 billion years • dominant form of life on Earth • live in every hospitable environment • > 100 trillion on and in human body • total mass exceeds all animal life • 10 000 species known • roughly 1% of believed total # of species
Eubacteria = BACTERIA • Sketch figure 6 from page 48 • On your sketch label: • cell wall • plasmid • ribosomes • flagella • pilli • capsule • Make sure to write down a function for each one of these structures
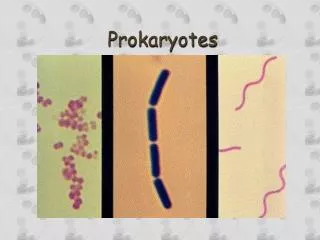
- There are 3 main shapes to bacteria Spirillum Coccus Bacillus - video
Many different and diverse evolutionary branches of the Domain Eubacteria • 6 main groups of human importance • Vary dramatically in energy and nutrient gathering Using table 1 on page 48 of the text, complete the chart for each bacteria. Include only the 2 most important key features of each bacteria
Reproduction Bacteria reproduce asexually and very quickly! -video - 1000 times faster than a eukaryotic cell Binary fission - 3 step process Step 1: Duplication of the chromosome Step 2: Cell elongates Step 3: Cell divides into two Daughter cells are identical to mother cell
Mutations • ease of evolution • genetic diversity Conjugation –exchange of genetic information; sexual reproduction Transformation –taking in of foreign DNA by the bacteria for use • horizontal gene transfer • positive/negative Endospore
Metabolism How an organism produces energy So where does a bacterium get its energy to move and reproduce? Autotrophic Heterotrophic -make own energy from inorganic compounds -need to ingest energy from organic compounds Animals and plants Bacteria Obligate aerobes –need oxygen to survive Obligate aerobes Facultative aerobes – live with or without oxygen fermentation
Bacteria: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly Spread through Europe 14th C Killed 30 – 60% of the population - approx 100 million people Swollen lymph nodes, fever, vomit blood -death in days The Bubonic Plague “The Black Death” Yersinia pestis
e. coli Found in the large intestine of warm-blooded animals Very important to scientific research –recomb DNA host Some different strains Escherichia coli • Good production of vit K and destroy harmful bacteria • Bad cause food poisoning • Ugly bloody diarrhea, gastrointestinal infections, death Walkerton May 2000 Farm runoff into nearby well Walkerton Public Utilities Commission Stan and Frank Koebel
Antibiotics • PATHOGEN: Infectious bacteria Leprosy Cholera Salmonella Tuberculosis • ANTIBIOTIC: substance that can kill or weaken micro-organisms; produced by bacteria fighting for nutrients overuse leads to resistance • Nitrogen fixation • Vit K and B12 production • MUTUALISM: relationship whereby each benefits
Domain Archaea • Very little known about this group • make up is unlike bacteria or eukaryotes • Play key role in ecosystems • low-oxygen; intestines; produce methan gas • salt-loving • extreme heat; hot springs, ocean vents • cold-loving; Arctic and Antarctic methanogens halophiles extreme thermophiles psychrophiles