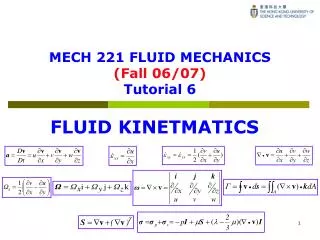
Tutorial 7_Review MECH 101
230 likes | 412 Vues
Tutorial 7_Review MECH 101. Liang Tengfei tfliang@ust.hk Office phone : 2358-8811 Mobile : 6497-0191 Office hour : 14:00-15:00 Fri. A chance to show what you have learned:. Statics structure in Equilibrium → the forces atcing on it Mechanics of material

Tutorial 7_Review MECH 101
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tutorial 7_Review MECH 101 Liang Tengfei tfliang@ust.hk Office phone : 2358-8811 Mobile : 6497-0191 Office hour : 14:00-15:00 Fri
A chance to show what you have learned: • Statics structure in Equilibrium → the forces atcing on it • Mechanics of material the force → stress and strain in each point→ deformation & break or not
Statics • Question choose draw build solve
Which free body should I choose? Solve the force from the pin C acting on the member DC and AB • remember which force you want • let the target force appear in you F.D.B • external force will appear in the F.B.D • Specify your free body
How to draw F.B.D? • Only external force will appear in the F.B.D • Search around the F.B. every thing contacting the F.B. will give it force. How about gravity?? • Draw all the force in F.B.D if you known the direction →draw the real direction. otherwise → assume a direction.
Build up equilibrium equations • Build up the equation base on the F.B.D the sign of the force and moment is base on the direction of the force in F.B.D usually force : same with the coordinate : + moment : counterclockwise : +
solve the force • Clarify the real direction of the force. • Use your intuition to check the answer.
C B A 45 O 100N Example 4m • The 100N weight of the rectangular plate acts at its midpoint. Determine the reactions exerted on the plate at B and C. Solution: Notice AB is a two-force member, so the reaction at B must be directed along the line between A and B.
C B 45 O 100N Solution 4m Apply the equilibrium equation:
Other things in statics • Replace the distributed load • Two force member
Mechanics of material Equilibrium equation Internal force stress statics Hook’s law observation deformation strain Equation of compatibility
P P A A P P L Normal Stress and Normal Strain Normal stress: force per unit area This equation is valid only if the stress is uniformly distributed over the cross section of the bar. Normal strain: elongation per unit length Remind strain is a dimensionless quantity
P P Hook’s Law and Poisson’s Ratio Hook’s law Note: A permanent strain exists in the specimen after unloading from the plastic region. Poisson’s ratio Poisson’s ratio is also a constant, a property of the material, and dimensionless Dashed means the original shape with out P
Example PL AE δ= Elongation → +δ, Contraction → -δ Tension → + P, Compression → - P Composite A-36 steel bar shown made from two segments AB and BD. Area AAB = 600 mm2 and ABD = 1200 mm2. Est = 210 GPa Determine the vertical displacement of end A and displacement of B relative to C.
Example PABLAB AABE PCDLCD ACDE +35kN x 0.75m x 106 1200mm2(210)(103)kN/m2 +75kN x 1m x 106 600mm2(210)(103)kN/m2 +35kN x 0.75m x 106 1200mm2(210)(103)kN/m2 -45kN x 0.5m x 106 1200mm2(210)(103)kN/m2 + + δA = δA/B + δB/C + δC/D = PBCLBC ABCE = + + = 0.61 mm = 0.104 mm Displacement of B relative to C (δBC)=
Shear Stress - single shear Shear stress: Bearing stress:
V m n a L p q V Shear Stress and Bearing Stress Shear stressacts tangential to the surface of the material. Average shear stress: Where Average bearing stress: Where d m n
Shear Strain and Hooke’s law in Shear Shear strain : change in the shape of the element When is small Hook’s law in shear
C B A 45 O 100N Example • The 100N weight of the rectangular plate acts at its midpoint. Determine the reactions exerted on the plate at B and C. • if the pin at C is connected by a double shear pin. Pin’s lenghth is 2.5cm (0.5, 1.5 , 0.5), The shear and bearing stress limit of the pin is 100MPa & 150MPa, if the safe factor is 1.5, what the minimum diameter of the pin? 4m
2. the bar AB has a rectangular cross-section. Its area is 10 mm2 . AB is glued together at pq, theta = 30 degree. the shear stress limit on this surface is 50MPa, will this bar break?