CHEMICAL REACTIONS
150 likes | 316 Vues
This resource provides an overview of chemical reactions, including reactants and products, types of reactions (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion), and the importance of balancing equations to uphold the law of conservation of mass. It includes examples and practice problems to reinforce learning about reactants' physical states, solubility rules, and the characteristics of chemical reactions. Ideal for students seeking to enhance their knowledge in chemistry.

CHEMICAL REACTIONS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHEMICAL REACTIONS http://www.fordhamprep.org/gcurran/sho/sho/lessons/lesson82.htm http://staff.imsa.edu/science/chemistry/web/Chemical%20Reactions%20Lab-revised.pdf http://chemicalparadigms.wikispaces.com/Chemical+Reactions
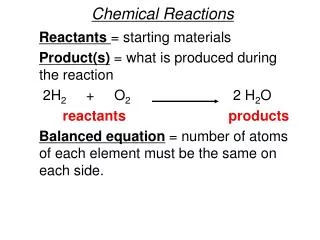
Chemical Reactions: • Reactants => Products • CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) => CO2 (g) + 2 H2 O (l) • The coefficients of a chemical reaction must be balanced in order to obey the law of conservation of mass.
Physical States • (s) solid, a precipitate formed • (l) liquid • (g) gaseous, • (aq) aqueous, substance dissolved in water • Diatomic Molecules: H2 , O2 , N2 , F2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2
Types of Chemical Reactions • Single Replacement • Synthesis • Decomposition • Combustion • Double Replacement
1. Combination or Synthesis Two or more substances react to form a single new substance. 2 Mg(s) + O2 (g) => 2MgO(s) Complete and Balance: a) Be + O2 => b) ___ + ____ => NaCl c) Al + S =>
Practice • 1) H2 + F2 => • 2) Al + Cl2 => • 3) ________ + _______ => KBr
2. Decomposition A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler products. 2 HI => H2 + I2 H 2 O2 H2 O + O2 Complete: • a) KClO3 => ____ + ____ + ____ • b) ______ => Li + Br2
3. Single Replacement One element replaces a similar o one in a compound. Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq)=> Cu(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) Ca + AgNO3 => Au + ZnBr2 =>
Reactivity of Halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 F2 + HCl => HCl + I2 => Br2 + MgI2 => AlF3 + Br2 =>
Simulation Single Replacement Reactions. • After performing all reactions, write your observations, write the equations and balance all. • http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/Greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/redox/home.html
4. Double Replacement Involves an exchange of positive ions between compounds. KI(aq) + HgCl2 (aq) => KCl (aq) + HgI2 (s) HNO3 + CaBr2 => http://web.fccj.org/~smilczan/Two5/DR.html http://www.fordhamprep.org/gcurran/sho/sho/lessons/lesson82.htm
Solubility Rules • All common compounds of Group I and ammonium ions are soluble. • All nitrates, acetates, and chlorates are soluble. • All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) • All sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, calcium, lead, silver, and mercury (I). The latter three are slightly soluble. • Except for rule 1, carbonates, hydroxides, oxides, silicates, and phosphates are insoluble. • Sulfides are insoluble except for calcium, barium, strontium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and ammonium
Write correct formulas for the products in these double replacement reactions and balance. • 1) CaCl2 + H3PO4 ---> • 2) K2CO3 + BaCl2 ---> • 3) Cd3(PO4)2 + (NH4)2S ---> • 4) Co(OH)3 + HNO3 --->
5. Combustion When a substance combines with oxygen, it produces an oxide: Na + O2 => Na2 O • When a hydrocarbon burns in the presence of oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water: • 2C4H10 (g) + 13 O2(g) => 8CO2(g) + 10H2O (g)
1. What is the reaction of combustion of the major component of gasoline, octane, C8 H18 • 2. What is the reaction of combustion of ethanol C2 H5 OH