CEPHALOSPORINS
200 likes | 967 Vues
CEPHALOSPORINS. BY: MS. SABA INAYAT ALI. DEFINITION. Any of various broad-spectrum beta- lactam antibiotics closely related to the Penicillins, that were originally derived from the fungus, Cephalosporium acremonium. INTRODUCTION. ACTION: Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis COMMON USE:

CEPHALOSPORINS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CEPHALOSPORINS BY: MS. SABA INAYAT ALI
DEFINITION • Any of various broad-spectrum beta- lactam antibiotics closely related to the Penicillins, that were originally derived from the fungus, Cephalosporium acremonium
INTRODUCTION • ACTION: Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis • COMMON USE: In surgical procedures- to reduce the risk of post- operative infections.
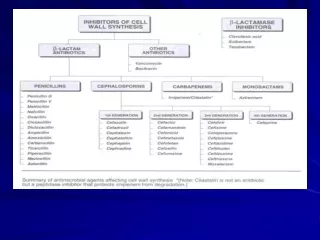
CLASSIFICATION • 4 Generations- based upon: • The spectrum of antimicrobial activity • Grouped w.r.t increased Gm. Negative & decreased Gm. Positive activity
FIRST GENERATION • Cefazolin • Cephalexin • Spectrum:Most Gm. +ve cocci (Strep, S.aureus), E.coli, proteus, Klebisella • Use: S.aureus infection, surgical prophylaxis
SECOND GENERATION • Cefoxitin • Cefuroxime • Cefaclor • Cefprozil • Spectrum: mainly effective gram negative bacteria, modest activity against gram positive bacteria • Use: primarily for upper & lower respiratory tract infections
THIRD GENERATION • Ceftriaxone • Cefotaxime • Spectrum: enhanced gm. –ve activity • Use: Meningitis, highly resistant & multi drug resistant Strepto pneumo along with vancomycin
FOURTH GENERATION • Cefepime • Spectrum: active against Strep, staphylo, aerobic gm. -ve
It is possible to convert penicillin V or Benzyl penicillin to a cephalosporin by chemical ring expasion. • The first generation cephalosprin Cephalexin, for example, can be made by this way. • Most cephalosporins used in clinical practice are semi-synthetics produced from the fermentation product cephalosporin C
Cephalosporium acrimonium • Most common in: • Soil • Plant debris • Rotting mushrooms
Cephalosporins • Cephalosporin C was first isolated in 1952. • Cephalosporin C is made as the fermentation product of Cephalosporium acremonium. • However, this form is not potent for clinical use. • Its molecule can be transformed by removal of an aminoadipic acid side chain to form 7-α aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA), which can be further modified by adding side chains to form clinically useful broad spectrum antimicrobials
Cephalosporins • Various side chains can be added to as well as removed from both 6-APA and 7-ACA to produce antibiotics with varying spectra of activities and varying degrees of resistance to inactivation by enzymes produced by pathogenic microbes.
Production • Fermentation conditions are rather similar to those with penicillin but methionine is added to increase production
Medium • The initial defined medium contained Glucose, Ammonium chloride, Methyl oleate, Metallic salts… little cephalosporin C was obtained • Production of cephalosporin C was induced by methionine, which cause the necessary thickening of the mycelium & raised cephalosporin C production to about 4g/L
Fermentation Conditions • fermentation is advantageously carried out at a temperature preferably about 25° C., • at a pH of from 5-8 and preferably about 6, • and for from 1-20 days, preferably 4-10 days.
Recovery of Antibiotic • The product is extracted from the culture fluid by adsorption on to carbon or resins rather than by solvent