Osmosis
140 likes | 475 Vues
Osmosis. Predict the direction of water flow given an osmotic situation. Determine the type of osmotic solution. Contrast effects of hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions on plant and animal cells. Background Information. Cells environments are mostly made of water.

Osmosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Osmosis Predict the direction of water flow given an osmotic situation. Determine the type of osmotic solution. Contrast effects of hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions on plant and animal cells.
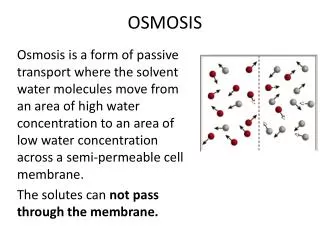
Background Information • Cells environments are mostly made of water. • Water can move across the phospholipid bilayer easily. • Cells are constantly subjected to the flow of water across their membrane because they CANNOT control it. • Triple threat! • Water is small, fast, and everywhere.
What is Osmosis? • A special form of diffusion—but only for WATER. • Osmosis: the diffusion of water across a membrane.
What are the different types of osmotic solutions? • Hypertonic: more water inside the cell. • Isotonic: even amount of water inside and outside of the cell. • Hypotonic: more water outside of the cell.
Isotonic • When the concentration of water is the same inside and outside the cell (equilibrium). • Water moves equally in and out of cells. • No change in the size of the cell.
Hypotonic • When the concentration of water is greater OUTSIDE the cell (less solutes outside). • Net water movement is INTO cell. • Ultimately, cells gain water and SWELL. • The end goal is always equilibrium!
Hypertonic • Concentration of water is greater INSIDE the cell (more solutes outside). • Net movement of water is OUT of the cell. • Ultimately, the cells lose water and SHRINK. • The end goal is always equilibrium!
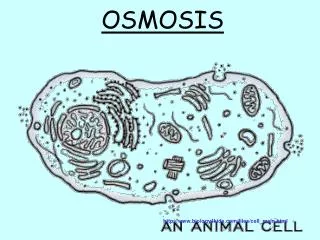
Inside the cell: 97% water 3% other molecules Outside the cell: 97% water 3% other molecules There is the same amount of water INSIDE and OUTSIDE of the cell, so the solution is ISOTONIC. There is no NET movement of water. There is no change in cell size.
Inside the cell: 97% water 3% other molecules Outside the cell: 99% water 1% other molecules There is more water OUTSIDE of the cell, so the solution is HYPOTONIC. Water will move INTO the cell and its size will get larger.
Inside the cell: 97% water 3% other molecules Outside the cell: 95% water 5% other molecules There is more water INSIDE of the cell, so the solution is HYPERTONIC. Water will move OUT of the cell and its size will shrink.
85% H2O 15% sugar 100% H2O 90% H2O 50% H2O Now you try…(Don’t forget—determine how much water you have, first!) Water moves OUT(mostly). This is HYPERTONIC. Water moves IN(mostly). This is HYPOTONIC.
75% H2O 30% sugar 25% sugar 20% salt 15% sugar Two more! Water moves IN & OUT. This is ISOTONIC. Water moves IN(mostly). This is HYPOTONIC.
Vocabulary • Osmosis • Hypotonic • Isotonic • Hypertonic • Lysed • Shriveled • Turgid • Flaccid • Plasmolyzed