Techniques for Solving Implicit Approximations in MODFLOW
100 likes | 241 Vues
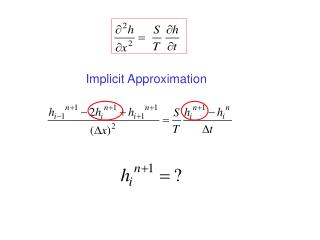
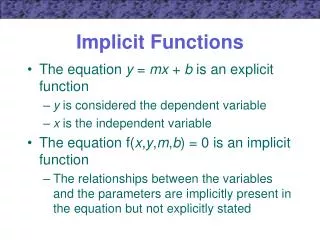
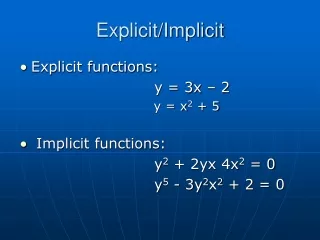
This document explores various methods for solving implicit approximations, including point iteration techniques such as Gauss-Seidel (G/S) and Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR), as well as direct matrix solutions. It also discusses combined approaches involving matrix solutions and iterations, exemplified by techniques like IADI, SSOR, and PCG2, which are commonly applied in MODFLOW. The general 3D equation used in MODFLOW is presented, emphasizing block-centered grids and the calculation of hydraulic properties like K values using harmonic means.

Techniques for Solving Implicit Approximations in MODFLOW
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Implicit approximation can be solved using: • Point iteration (G/S, SOR) • Direct (matrix) solution • Combination of matrix soln and iteration
Examples of solution techniques that combine matrix solution with iteration: IADI (see chapter 5 of W&A) SSOR* SIP* PCG2* *Used in MODFLOW
General 3D equation used in MODFLOW Block centered grid xi i-1 i i+1 xi-1/2 xi+1/2
K values in the space between nodes is calculated using the harmonic mean
Types of Layers (LAYCON array) Confined Unconfined Convertible (Useful to think in terms of a layer transmissivity.)