Speciation and Extinction
290 likes | 529 Vues
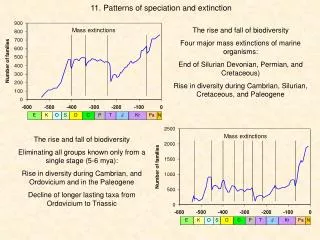
Speciation and Extinction. Big Idea 1: The process of Evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Essential Knowledge. 1C1: Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history.

Speciation and Extinction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Speciation and Extinction Big Idea 1: The process of Evolution drives the diversity and unity of life
Essential Knowledge • 1C1: Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. • 1C2: Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. • 1C3: Populations in nature continue to evolve.
A group of individuals capable of interbreeding and exchanging genetic info to produce viable, fertile offspring. Species YES Panda Babies! NO Dog-Cat Babies!
Speciation • Creation of a new species • Usually occurs when 2 pops diverge from a common ancestor
Speciation Can Be Slow…. • Very gradually, over a long time, the population changes (gradualism). Change is slow, constant, and consistent (Darwin).
Speciation Can Be Fast… • Bursts of change followed by quiet periods (Punctuated Equilibrium, Eldredge and Gould, 1972)
What Could Cause Bursts?? • Sudden, quick changes in the environment leads to more available niches!
Geographic Isolation Separation of pops by a geographic barrier exposes species to new environmental conditions.
Reproductive Isolation • Biological factors (barriers) that stop 2 species from producing viable, fertile offspring • Can be pre/post zygotic barriers
Example: Polyploidy • More than 1 set of chromosomes. • Ex: Wheat: strains that are diploid(2 sets),tetraploid(4 sets) durum or macaroni wheat, hexaploid(6 sets) bread wheat. • Will not interbreed with each other.
Prezygotic Barriers Goal: To impede mating/fertilization! • Habitat isolation: no/rare contact • Temporal isolation: mate at diff. times of yr. • Behavioral isolation: behavior mating rituals. • Mechanical isolation: Morphological differences
Postzygotic Barriers Goal: Prevent a hybrid zygote from being a viable adult • Frail/Weak Hybrids • Sterile Hybrids
Extinction • Occurs rapidly at times of ecological stress.
On a Positive Note.. • Extinction opens up available niches (jobs) and leads to new species creation.
Evolution Continues to Occur… • Activity in class…