Understanding Arrays and Data Types: Practical Examples
80 likes | 231 Vues
This article explores the concept of arrays in programming, specifically focusing on integer and string arrays. It delves into the creation of one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays, illustrating their characteristics with practical examples, such as jagged arrays and 2D arrays. Key concepts include accessing array elements using index numbers, initializing lists with values, and the distinctions between different array types. This guide serves as a solid introduction for developers to efficiently utilize arrays in their projects.

Understanding Arrays and Data Types: Practical Examples
E N D
Presentation Transcript
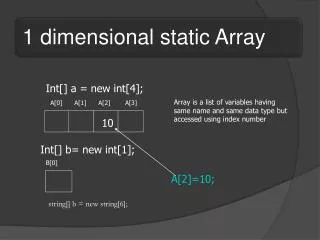
Int[] a = new int[4]; Array is a list of variables having same name and same data type but accessed using index number A[0] A[1] A[2] A[3] 10 Int[] b= new int[1]; B[0] A[2]=10; string[] b = new string[6];
String[] n; n= new string[3]; n[0]=“faisal”; n[1]=“Israr”; n[2]=“javed”; n is nothing n[0] n[1] n[2] n[0] n[1] n[2] faisal Israr javed String[] n={“faisal”,”Israr”,”javed”};
string[] weekDays = new string[] { "Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat" }; int[] array3; array3 = new int[] { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 }; // OK array3 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; // Error
int[,] n = new int[2,3]; Int[,] n = new int[1][1]; n[0,2] 0 1 2 n[0,0] 0 0 0 1 int[, ,] n = new int[2,3, 3]; 0 1 2 n[1,0,2] 0 1 2 0 1
int[,] arr2D = new int[,] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } }; int[, ,] arr3D = new int[,,] { { { 1, 2, 3 } }, { { 4, 5, 6 } } }; int[,] array4 = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } }; int[,] array5; array5 = new int[,] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } }; // OK array5 = {{1,2}, {3,4}, {5,6}, {7,8}}; // Error
int[][] a= new int[][]; a = new int[0][3]; a= new int[1][1]; Int[][] a; a=new int[1][1] {} A[0]=new integer[3]{} A[1]=new integer[1]{} 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 3 1 0 1 a[1][1] a[1][1]
int[][] jaggedArray2 = new int[][] { new int[] {1,3,5,7,9}, new int[] {0,2,4,6}, new int[] {11,22} }; int[][,] jaggedArray4 = new int[3][,] { new int[,] { {1,3}, {5,7} }, new int[,] { {0,2}, {4,6}, {8,10} }, new int[,] { {11,22}, {99,88}, {0,9} } };