Parathyroid Glands
180 likes | 724 Vues
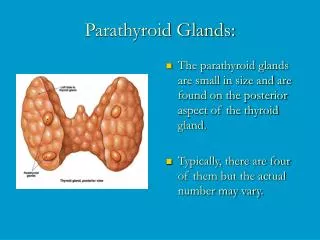
Sam Pandey and Ben Cherry P:6 1/13/13. Parathyroid Glands. Location. We normally have 4 parathyroid glands total Located in the neck Exist behind the Thyroid gland Exist in groups of two Two on the left of the thyroid and two on the right. Hormones .

Parathyroid Glands
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sam Pandey and Ben Cherry P:6 1/13/13 Parathyroid Glands
Location • We normally have 4 parathyroid glands total • Located in the neck • Exist behind the Thyroid gland • Exist in groups of two • Two on the left of the thyroid and two on the right
Hormones • Parathyroid Gland secretes two main hormones • The Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)-Positive hormone • Calcitonin-Negative hormone
Effects on human body • Both PTH and calcitonin regulate calcium levels • PTH increases the level of calcium and phosphorous if level is low (osteoclast activation) • PTH acts upon both bones and kidneys • Withdraws calcium from urine • Calcitonin inhibits osteoclasts
Roles on homeostasis • Parathyroid hormone controls calcium • Calcium plays an enormous role in maintenance of homeostasis • Effects neuromuscular excitability, blood clotting, cell membrane permeability and functioning of certain enzymes • Calcium is very important…
Facts about calcium • The most important roles of calcium are… • Provide means for electrical impulses to travel • Provide electrical energy to nervous system • Provide electrical energy to muscular system • Provide strength to skeletal system
Positive Feedback Mechanisms • Low blood calcium level leads to… • Increased secretion of PTH • Further osteoclast activation • Increase in bone matrix breakdown • Calcium transported to bloodstream • Blood-calcium level increase • Ultimately achieving normal BCL
Negative feedback (antagonistic) • High blood calcium leads to… • Increased secretions in calcitonin (antagonistic hormone) • Reduced or inhibits osteoclast activity • Decrease in bone matrix breakdown • Ultimately achieving normal BCL
Trouble • Hyperparathyroidism- a disease in which the parathyroid gland secretes too much PTH. • Blood calcium levels soar • Life threatening • Can kill in an average of 20 years
Hyperparathyroidism • Symptoms • Constipation • Lethargy • Muscle weakness • Muscle spasms • Osteoporosis • Coma • Death
Hypoparathyroidism • A rare condition in which body secretes low levels of PTH • Low production of PTH ultimately leads to low ionized levels of calcium in blood • Also causes increased levels of phosphorous • Lethal if not treated
Symptoms • Hypocalcemia • Increased neuromuscular irritability • Muscles spasms • Convulsions • Seizures • Tingling sensations • Painful menstruation • death
Treatments • Hyperparathyroidism is very curable if dealt with correctly • Surgeries are available • Cure rates are usually in the 90-100% range • Hypoparathyroidismis not curable by surgery • Pills and other supplements are available • Patients must take these supplements often times throughout their life
Sources • Anthony’s Textbook of Anatomy & Physiology • http://www.parathyroid.com/parathyroid.htm • http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypoparathyroidism/basics/definition/con-20030780 • http://www.medicinenet.com/hyperparathyroidism/article.htm