Database management system
470 likes | 735 Vues
Sayed Ahmed Computer Engineering, BUET, Bangladesh MSc, Computer Science, U of Manitoba, Canada Owner/President/Architect/Developer Justetc (Just et cetera) Technologies http://www.justetc.net http://sayed.justetc.net sayed@justetc.net. Database management system.

Database management system
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sayed Ahmed Computer Engineering, BUET, Bangladesh MSc, Computer Science, U of Manitoba, Canada Owner/President/Architect/Developer Justetc (Just et cetera) Technologies http://www.justetc.net http://sayed.justetc.net sayed@justetc.net Database management system
Free Training by Justetc • Training and Education in Bangla: • http://Bangla.SaLearningSchool.com • http://Blog. SaLearningSchool.com • Training and Education in English: • http://www.SaLearningSchool.com • http://English.SaLearningSchool.com • http://www.SitesTree.com --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- • Ask questions and get answers • http://Ask.JustEtc.net --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- • Offline IT Training: • http://University.JustEtc.net
Learning Objectives • Concept of Database and Database Management System • Activities of a Database Management System • What is a Relational Database Management System • Features of Relational Database Management System
Learning Objectives • Create database • Concept and explain the importance of Data Security • Data Encryption • Importance • Methods • Querying Database: Query Language: SQL • Uses of Databases
What is a Database? • Database means • Data storage • A good/organized/efficient way of storing data • You can store all the information of a public library/bank into a database • How are information stored in computers? • In files; you know it when you learn to use computers • Files are stored in computer hard drives, USB sticks, memory cards
What is a Database • Is there anything different of storing data by a database • Not much, databases also store data in files • However, a database stores data in files in a very organized way so that it becomes easier to • Insert new data into the file/files • Easier to search, sort, and retrieve data from those files
What is a Database • Let’s see, you can store all information of a bank in a single computer file • All bank account information • All employee information • All account holder information • All branch and department information • You can keep them in a single file; but can be very difficult to find something useful fast; also inserting data and managing the file can be difficult
What is a Database • Now you can store all data in multiple files; just divide the original file into multiple files; • Still if you do not organize the files or the data in them, it can be very difficult to work with them • In a database, information are kept eventually in computer files • However, a database will use a good strategy on how to store those data into files • Databases will store the data in many files • Will store in such a way so that it becomes easier to work with the files and the data • In real life, we have systems and software that knows about the strategy and helps to deal with those files and data for efficient storing, searching, retrieving, doing operations on the data and store the result in the same database • We call such systems and software to be the Database Management System
What is a database • One strategy • Keep one type of data into one file • Such as in one file, store all bank account holders personal information • In another file, keep the details of all the bank accounts • In another file, keep the association between these accounts and account holders • If the number of records in a file is two many, divide the files into multiple files but keeping the same type of information; find a way to keep track which files are related • Create some other files to keep track of which files store what • Create some other files that can store the location/address/position of a particular data in other files [index file]
What is a Database Management System • If we have software that implements the strategy described above, can be called a DBMS • When we feed data into it, if it can store the data using that strategy and provides ways to manipulate the data in an efficient way • Then we can call this software to be a DBMS • DBMSes usually display data in tabular format (row/column - format)
Database and Database Management Systems • From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia • A database • is an organized collection of data. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring this information. For example, modeling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies • Database management systems (DBMSs) • are specially designed applications that interact with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data. A general-purpose database management system (DBMS) is a software system designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Oracle, SAP, dBASE, FoxPro, IBM DB2, LibreOffice Base and FileMaker Pro. A database is not generally portable across different DBMS, but different DBMSs can inter-operate by using standards such as SQL and ODBC or JDBC to allow a single application to work with more than one database.
Activities provided by a DBMS • DBMS can create a database • i.e. Create the initial structure of the database • Allocate space and saves the database in the hard drive • Control who can use a database • Take data from user and record and store it somehow • Organize data • In meta files or in actual data files • Provide means to search and display the data • Provide security of the data • Maintain the integrity of the data
Advantages of a DBMS • Improved availability • To different users, efficient retrieval of data • Minimized redundancy • Data are organized in a way so that the same data are not stored in multiple places/files • Accuracy • Can keep data consistent as 1. redundancy reduced and 2. data is available through one interface (DBMS interface)
Advantages of a DBMS • Program and file consistency • Standardizes the storing of data; so others can use it easily • User-friendly • Easier to deal with [usually provide friendly interface] • Improved security • Control who can access the database
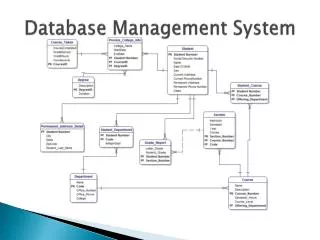
Relational Database Model • Just a strategy to store and manipulate data • The strategy we talked about indirectly refers to relational model • Based on relational model • What is a relational model? • it is a method of structuring data using relations, which are grid-like/matrix-like mathematical structures consisting of columns and rows • Table is the physical manifestation of a relation in a database • So data are stored in tables (row/column wise) in Relational Database Models
Relational Database Model • It is composed of one or more tables [to represent data] • Tables also represent the relations/associations of different related data • So here, we have tables of data • Tables has columns called fields • Tables are linked/related to other related tables by common columns/fields • Primary key/foreign key concept
Relational Model for A Library • Books: Book Information • Id, title, published, price • Authors: Author Information • Id, name, SIN, address • Members: member information • Id, name, SIN, address, phone, email • Book-Borrowers: • Relation between books and members • Bookid, memberid, date
Features of Relational DBMS • Provide easy ways to create tables • Provide easy ways to create relations among tables • Provide ways to insert, update, search data in a table or from multiple tables • Provide ways to validate data at insertion • Provides language such as SQL for data insertion, update, and search • Support multiple views of data
Features of Relational DBMS • It is easy to create application software having relational database in the backend
Usage of Relational DBMS • Airlines reservation system • Banking management system • Online banking system • Hospital operation management systems • Library management system
Creating Databases • What does it involves? • In DBMS, usually there is an option to create database • It may ask for initial size of the database • How to increment the size of the database • Character encoding of the database • Model to use for creating the database (relational, object oriented) • Security/access control for the database • Path to store the database files • Then it will create the basic structure of the database and store it in hard rive.
Creating Databases • The basic element of database creation is fields/columns • You have to identify the different concepts/object and relations among concepts [in the system] • For each, concept/object, you have to identify fields • Then create tables for each of the concepts (and for relations sometimes) • For each table define the fields/columns • Identify data types and length for each column/field and specify it when creating tables
Data Types for Fields • Numeric • Byte • Bit • Int • Long • Double • float
Data Types for Fields • Text • Text • Char • Varchar • Date, DateTime • Currency
Query Language: SQL • Types • Select • Selecting data by table fields • Parameter • Query by filling information in dialog bixes • Crosstab • Based on conditions • Action • Delete, update, append
Sorting and Indexing • Sorting • Is to arrange/sort data • Low to high: Ascending • 1, 2, 3, 4..100 • A ant boy cat • High to low: descending • 100,99,98....1 • Cat boy ant a
Indexing • Create an index (information about the position) of the data • Indexing is not actually sorting the data but keeping track of the locations of the data • Index can keep track of the data • by ascending values or in descending values (of the data) • i.e. In index file there will be positions/addresses of the data, the addresses will be kept in the order of the values of the data
Indexing • Data • 4 • 2 • 100 • 50 • Index of the data in ascending value of the data • 2, 1, 4, 3
Indexing • Advantages • Can help to find the data faster when index by one field • Increases the performance of different database operations • Disadvantages • More ram used • Data entry can take time for multiple field based index • When index with multiple fields, data editing can take longer
Relation Types • Degree of relations • Unary -1 • Binary – 2 • Ternary – 3 • Relation Types: among tables (concepts/objects in the system) • One to one • One to Many or Many to One • Many to Many
Use of Database for Government • E-government • E-governance • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E-Governance • E-Governance is the application of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for delivering government services, exchange of information communication transactions, integration of various stand-alone systems and services between Government-to-Citizens (G2C), Government-to-Business(G2B),Government-to-Government( G2G) as well as back office processes and interactions within the entire government frame work.
E-government • E-government • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E-Government • E-Government (short for electronicgovernment, also known as e-gov, Internet government, digital government, online government, or connected government) is digital interactions between a government and citizens (G2C), government and businesses/Commerce (G2B), government and employees (G2E), and also between government and governments /agencies (G2G). Essentially, the e-Government delivery models can be briefly summed up as (Jeong, 2007):[1] • G2C (Government to Citizens) • G2B (Government to Businesses) • G2E (Government to Employees) • G2G (Government to Governments) • C2G (Citizens to Governments)
Data Security • Data is important for an organization or government or a person • Data should not be able to be accessed by unauthorized person • Data when stored in the office or when transferred over the internet, it should not be able to be accessed by unauthorized person such as hackers, or competitors
Methods to Provide Data Security • Restrict access to the computer (password protect) • Restrict access to the database (password protect) • Use firewalls so that outsiders cannot access • While sending data encrypt(unreadbale format) data
Data Encryption • Changing/converting the data to unreadable format while transferring • Usually using some methods/algorithms data are encrypted. • Some encryption methods use keys • Encryption Ingredients • Plaintext : text to be sent • Ciphertext : encryted text • Encryption algorithm : method to encrypt • Key : used in encryption or decryption
Encryption Types • Types • Secret-key encryption • Public-key encryption • Secret-key encryption • Same key used for encryption and decryption • Both sender and receiver know the key • Public-key encryption • Sender: one key to encrypt : private to sender • Receiver: another key to decrypt : private to receiver • One more key, known to both
Encryption Methods/Algorithms • Caesar code • DES • IDEA • RSA
Further Study • Encryption • http://www.salearningschool.com/searchResult.php?queryStr=encryption&submit=Search+Database • Encryption example • http://www.salearningschool.com/displayArticle.php?table=Articles&articleID=1355 • Encryption algorithms • http://www.cse-cst.gc.ca/its-sti/services/crypto-services-crypto/ca-ac-eng.html • Choosing encryption methods for SQL Server • http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms345262.aspx
Our Addresses • Trudelle Street, Toronto, Canada • sayed@justetc.com • Shimultuly, Gazipur, Bangladesh • Justetc Computers • Habib Complex, 2nd Floor • rafik@justetc.com (01942747702)
References • DBMS Theory • http://www.salearningschool.com/index.php?table=Articles&categoryID=6&category=DBMS%20Theory • Database Systems • http://www.salearningschool.com/index.php?table=Articles&categoryID=2&category=Database%20Systems • MySQL DBMS • http://www.salearningschool.com/searchResult.php?queryStr=mysql&submit=Search+Database • Indexing vs Sorting • http://docs.acl.com/acl/920/index.jsp?topic=/com.acl.user_guide.help/data_analysis/c_sorting_versus_indexing.html