Non-executive Directors
310 likes | 761 Vues
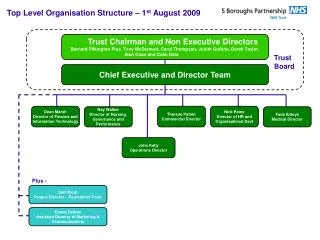
Non-executive Directors. Role in Corporate Governance. Who is a NED?. A member of Board of Directors of a company who has no executive responsibility in the company. His presence is intended to improve the quality of decision making at board level.

Non-executive Directors
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Non-executive Directors Role in Corporate Governance
Who is a NED? • A member of Board of Directors of a company who has no executive responsibility in the company. • His presence is intended to improve the quality of decision making at board level. • He still has all the fiduciary and statutory responsibilities.
Importance of NEDs • Just as it has been assumed that Board of Directors is key to good corporate governance, it has also been taken for granted that presence of INEDs is what makes a Board a balanced or good board. • This is a dangerous misconception.
Why have NEDs? • To bring a range of skills and experience to the deliberations of the Board. • To act as a counter-balance to the influence of one segment of the board over the others.
Sources of getting NEDs • EDs in other companies • NEDs or chairmen of other companies • Professionals • Former civil servants • Public figures
Types of NEDs • Nominees / representatives • Independent (INEDs) • In general context, NEDs are assumed to be INEDs, unless otherwise stated. However, in Pakistan INEDs are almost non-existent.
Higgs Report (2003) NEDs can help in: • Strategy formulation • Performance evaluation • Risk management • Remuneration through serving on relevant committees
How many NEDs? Combined Code 2003 prescribes: • At least half of the board, including chairman, should be NEDs • All or most NEDs should be INEDs. • The Pak scene
NEDs on board committees No legal restrictions, but: • Audit Committee • Nominations Committee • Remuneration Committee should have majority of NEDs
Independence of NEDs • If an NED is not independent, he is of no real use to the company. • Using NEDs to simply comply with law or practice is not healthy. • Company should be prepared to put up with the independence of NEDs. • Independence is a shade of integrity.
Measures of Independence • Relationship with EDs /CEO • Immediate past association • Material interest in the company: • Income from the company • Stake in the company’s profit/share price • Inter-locking directorships • Length of tenure
Protecting Independence • It is a state of mind; rules cannot ensure independence. • Company must want to have independent NEDs. • In the first place, Nom-Committee should be fiercely independent. • The Pakistani scene
The Senior INED • Source of collecting gripes • Internal • External • De facto Vice Chairman • Should meet regularly with INEDs
Hermes Guidelines Things INEDs should look at: • Appointment process • Skills and attitude required • Perspective on the company • Investment in the company
NEDs and Institutional Investors • Common source of appointment • Induction program • Liaison between the two • Maintaining independence
Criticism on INEDs • Insufficient real knowledge • Insufficient time • Insufficient opportunity to meet all stakeholders • Influence of EDs • Reciprocal treatment • Law does not help INEDs
Tyson Report (2003) • Advice • Monitoring: • Implementation of strategy • Legal and ethical performance • Validity and adequacy of financial statements
Essential Qualities • Integrity / ethical standard • Sound judgment • Ability and willingness • Interpersonal skills