Unit 8: Acids and Bases
230 likes | 404 Vues
Unit 8: Acids and Bases. Correlates to T opic 10 in review book, pages 174-188. Unit 8: Acids and Bases. Acids = substances that react with a base; often has a low pH May be strong or weak Actual definition depends upon the type of acid/base .

Unit 8: Acids and Bases
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 8: Acids and Bases Correlates to Topic 10 in review book, pages 174-188
Unit 8: Acids and Bases • Acids = substances that react with a base; often has a low pH • May be strong or weak • Actual definition depends upon the type of acid/base • Bases = substances reacting with an acid; often has a high pH • May be strong or weak • 3 major types of acids and bases here
Characteristics of Acids and Bases • Acids: • Taste sour • Conduct current in solution • React with bases to form water and salt • React with some metals to make H2(g) • Low pH • Bases: • Taste bitter • Slippery/soapy feeling • Conduct current in solution • React with acids to form salt water • Have low pOH or high pH
II. Types of Acids and Bases • 1. Arrhenius • 2. Bronsted-Lowry
1. Arrhenius Acid/Base • Acid = substances that release hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions • proton donors • Ex.] HCl H+ + Cl- • Base = substances that release hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions • Hydroxide donors • Ex.] NaOH Na+ = OH-
2. Bronsted-Lowry Acid/Base • Acid = any substance that can donate hydrogen ions in solution • Proton donors Ex.] HCl H+ + Cl- • Base = any substance that can accept hydrogen ions in solution • Proton acceptors Ex.] NH3 + H+ NH4+
Lewis Acids and Bases [non-Regents] • Acid = any species that can accept an electron pair from another species in solution • Ex.] H+ + NH3 • Base = any species that can donate an electron pair to another species in solution NH4+
III. Strengths of Acids and Bases • STRONG acids/bases will completely dissociate [ionize] in solution • Ex.] HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, NaOH, KOH, etc. • WEAK acids/bases produce very few ions per molecule in solution • Ex.] vinegar, H3PO4, formic acid, citric acid, etc.
Acid and Base Conjugates • Acid/Base Conjugates = species that are formed in solution as a result of the dissociation of an acid or base • Ex.] HCl + NaOH Na+ + Cl- + HOH • Cl- is the conjugate base • Na+ is the conjugate acid
IV. Titrations • Titration = method used to determine the pH of an unknown solution • Process to find the concentration of an unknown acid/base by neutralizing it with a base/acid of known concentration • An indicator signals the equivalence point and tells that the neutralization is complete
Titrations, [continued] Uses burets, a standard solution of known pH, an indicator, and a fixed volume of a solution with an unknown pH Titration Formula: MaVa = MbVb • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u9nOIZDdvRw
Acid-Base Reactions Acid + Base = Salt + water Acids and bases neutralize each other H+ + OH- H2O
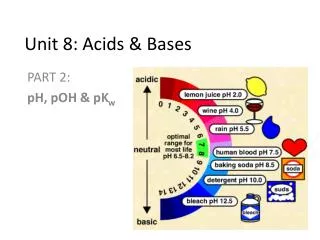
V. pH and pOH • pH = the scale, 0-14, that defines the acidity or basicity of a solution • Based on the concentration of hydrogen ions • 0-6 = acid • 7= neutral • 8-14 = base
pOH • pOH = the measure of the concentration of OH- ions in solution • Opposite of pH • Scale 0-14 • 0-6 = strong base • 7= neutral • 8-14 = acidic
Relating pH and pOH pH + pOH = 14 always! pH = -log[H+] pOH = -log[OH-]
B. pH and pOH Calculations Ex. 1] What is the pH of a solution containing 9.15 x 10-6 M H+? Ex. 2] What is the pH of a solution containing [OH-] = 8.11 x 10-5 M in 350.mL of solution?
C. Indicators • Indicators = compounds that change color when the pH changes • Color changes indicate the pH of the solution! • Use several indicators to pinpoint the final pH!
Indicators: Table M • Find the pH using the indicator and its color in the solution… Tutorial on indicators: http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/AcidsBases/Indicators.htm