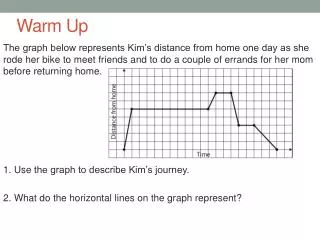
Warm-up
140 likes | 304 Vues
Warm-up. Write the formula for the following: Lithium Iodide Potassium hydroxide Magnesium oxide Name the following compounds: Na 2 O MgCl 2 CaSO 4 What is a binary compound?. Acids and Bases!!!. Definitions of acid and base Strong acid/strong base - definition

Warm-up
E N D
Presentation Transcript
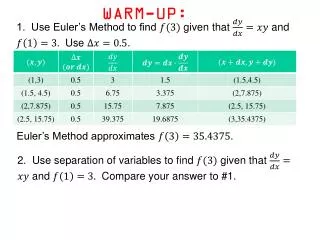
Warm-up • Write the formula for the following: • Lithium Iodide • Potassium hydroxide • Magnesium oxide • Name the following compounds: • Na2O • MgCl2 • CaSO4 • What is a binary compound?
Acids and Bases!!! • Definitions of acid and base • Strong acid/strong base - definition • Some common household examples of each • What formulas may look like (start with, end with, examples) • Properties of acids and bases • pH scale – How do you determine acid or base
Acids and Bases Whitaker 14 May 2014
Acids • Contains more Hydrogen ions (H+) or Hydronium ions (H3O+) than hydroxide ions (OH-) • Formulas start with Hydrogen • pH less than 7 • Properties • Sour taste • React with metals to produce H2 • Reacts with bases to produce a salt and water. • Changes Phenolphthalein clear • Common Acids • Acetic Acid (Vinegar) • Sulfuric Acid (Battery Acid) • Citric Acid (Lemon Juice/Orange Juice/Lime Juice)
Bases • Contains more hydroxide ions (OH-) than Hydrogen ions (H+) or Hydronium ions (H3O+) • Formulas generally end in -OH • pH greater than 7 • Properties • Bitter taste • Feel Slippery/Soapy • Reacts with acids to produce a salt and water. • Changes Phenolphthalein pink • Common bases • Sodium Hydroxide (Drano) • Magnesium Hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia/Antacid) • Sodium Hypochlorite (Bleach)
Naming Bases • These are named just like normal compounds that we’ve already learned about: • NaOH – Sodium Hydroxide • LiOH • Ca(OH)2 • KOH
Naming Acids • There are two types of acids: • Oxyacids • Binary Acids • The type of acid determines how it will be named.
Oxyacids • Contain Polyatomic Ions (will have more than two elements!) • Notice polyatomic ions generally end in either –ate or –ite. • If the polyatomic ends in –ate change the –ate to –icand add acid to the name. • Ex. H2SO4 • If the polyatomic ands in –ite change the –ite to –ous and add acid to the name • Ex. HClO2
Example • Name the following Oxyacids: • HClO3 • H2SO3 • H2CO3 • HNO3 • Write the formula for: • Chlorous acid • Sulfic acid • Nitrous acid
Binary Acids • Contain ONLY two elements!! • Take the root word of the anion (negative ion) and place it into the pattern of hydro_______-icacid • Ex. HCl
Example • Name the following binary acids: • HI • HBr • Write the formula for the following binary acids: • Hydrochloric acid • Hydrofluoric acid
Mixed Examples • Write the formula or name of the following acids: • Acetic Acid • HNO3 • Hydrofluoric acid • H2SO4 • Sulfous acid • HBr
What did you learn today?? • Acids exist at what pH range? • Bases have what taste? • What happens when you mix an acid and a base? • Name the following: • HCl • HClO • Write the formula for the following: • Hydroiodic acid • Chromic acid