Comprehensive Guide to Scalp Anatomy & Functions
110 likes | 389 Vues
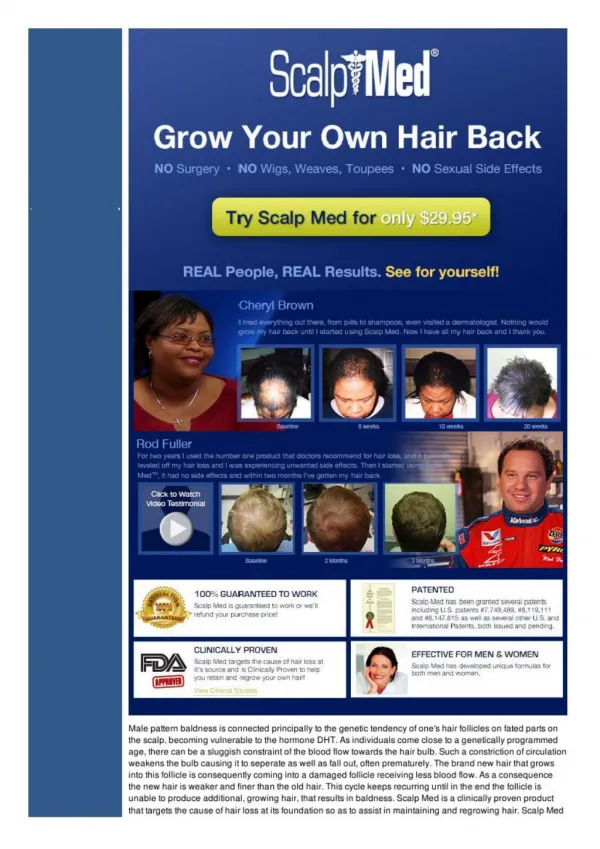
Discover the intricate layers, muscles, nerve supply, arterial and venous drainage, and clinical points of the scalp. Learn about its extension, layers, and crucial components for a deeper understanding.

Comprehensive Guide to Scalp Anatomy & Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scalp • Extension and Layers. • Muscles. • Nerve supply (sensory, motor). • Arterial supply. • Venous Drainage. • Lymph drainage. • Clinical points.
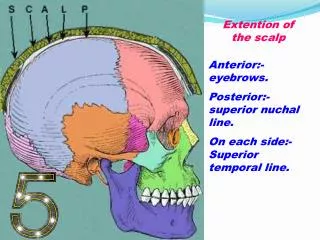
Extension and layers • It covers the vault of the skull and it extends: • Anteriorly: to the eyebrows. • Posteriorly: to the superior nuchal lines. • Laterally: to the temporal lines. • It has five layers: Skin, Connective tissue, Aponeurosis, Loose areolar tissue and Pericranium.
1. Skin • Thick. • Hair bearing. • Contains numerous sebaceous glands.
2. Connective tissue • Under the skin and connecting it to the underlying aponeurosis forming a thick one moving unit. • Fibro-fatty, the fat is tightly backed inside fibrous loculi. • Numerous arteries and veins are located in this layer.
3. Epicranial aponeurosis • Thin tendinous sheet, uniting the two bellies of occipito-frontalis muscle. • Laterally, it is attached to the temporal fascia.
4. Loose areolar tissue • Occupies the subaponeurotic space. • Loosely connects the superficial 3 layers to the 5th one (pericranium). • Contains small vessels, emissary and diploic veins.
5. Pericranium • The periosteum covering the outer surface of the skull vault. • It is limited to the edges of the bone and it is connected with the endocranium at the sutural joints.
Muscles of the scalp Occipito-frontalis • Origin: occipital belly from the highest nuchal line. Frontal belly from the skin and superficial fascia of the eyebrows. • Insertion: both bellies are inserted into the epicranial aponeurosis. • Nerve supply: occipital belly from posterior auricular branch of facial nerve and frontal belly from temporal branch of facial nerve. • Action: moves the superficial 3 layers together, and raises the eyebrows
Nerve Supply of Scalp • Sensory nerves of the anterior half are branches of trigeminal nerve: • Supratrochlear n. (ophthalmic n.). • Supraorbital n. (ophthalmic n.). • Zygomatico-temporal n. (maxillary n.). • Auriculo-temporal n. (mandibular n.). • Temporal branch of facial nerve is the motor nerve of the muscles of anterior half of the scalp.
Nerve Supply of Scalp • Sensory nerves of the posterior half are branches of cervical spinal nerves: • Greater occipital nerve (dorsal ramus of 2nd cervical nerve). • Lesser occipital nerve (C2 from cervical plexus). • Third occipital nerve (dorsal ramus of 3rd cervical nerve. • Great auricular nerve (C2,3 from cervical plexus). • Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve is the motor nerve of the muscles of posterior half of the scalp.