European Imperialism
90 likes | 463 Vues
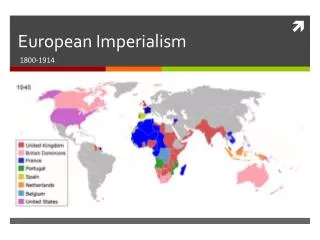
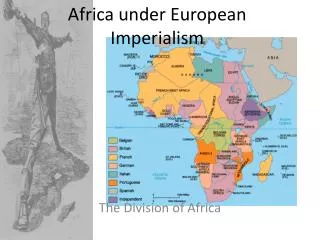
European Imperialism. 1800-1914. What is Imperialism?. When a powerful nation seeks to extend control or influence over less powerful nations. Goal is not necessarily to control territory, but instead to acquire resources and profit from them. Occurred globally during this period.

European Imperialism
E N D
Presentation Transcript
European Imperialism 1800-1914
What is Imperialism? • When a powerful nation seeks to extend control or influence over less powerful nations. • Goal is not necessarily to control territory, but instead to acquire resources and profit from them. • Occurred globally during this period.
European Motives for Colonization • Economic • Political • Cultural/Religious
Economic Motives • European nations were going through their Industrial Revolution. • Increased production = increased demand for raw materials • Other areas of the world were filled with raw materials. • Industrial nations began looking for new markets (groups of people to sell to)
Political Motives • Nationalism (pride and loyalty to one’s nation) was spreading throughout Europe nations. • European nations were trying to become more powerful than the next. • Colonies were viewed as status symbols and sources of $ and power.
Cultural/Religious Motives • Europeans were ethnocentric and believed they had a duty to their culture (religion, language, clothing, etc.) to the rest of the world. • Some people went to Africa for religious reasons. • They thought the Christian religion was superior, and wanted African to adopt their beliefs.
European Government in Colonized Areas Direct Rule Indirect Rule Great Britain British governor and a council of advisors would make colonial laws Local ruler had some power • France, Germany • Imperial power controlled all levels of government • Assimilation – people of the colonies would abandon their customs and adopt those of the imperial nation
Benefits and Cost of Imperialism Benefits Costs Most colonized did not accept European customs European Industry and institutions did not benefit the colonized Led to conflicts between tribes Millions of colonized were killed during the resistance. • New agricultural techniques were introduced • Medicine • Constructed roads and railroads