11-1 Tangent Lines
90 likes | 211 Vues
This guide explores the concept of tangents to circles, including definitions, theorems, and angle measures. A tangent is a line that intersects the circle at exactly one point, known as the point of tangency. The essential theorem states that a tangent line is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency. Additionally, we cover examples of finding tangents and determining angle measures in quadrilaterals. This resource is perfect for students learning about circle geometry and the relationships between tangents and radii.

11-1 Tangent Lines
E N D
Presentation Transcript
11-1Tangent Lines Objective: To use the relationship between a radius and a tangent.
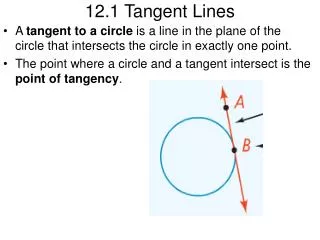
Tangent to a circle Point of tangency A line in the same plane of a circle that intersects the circle in exactly one point. The point where a circle and a tangent intersect. Vocabulary
Theorem 11-1 • If a line is tangent to a circle, then the line is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency. A P B O
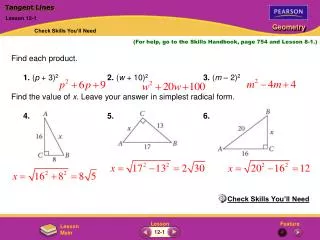
#1 Finding Angle Measures • is tangent to . Find the value of x. D E xo O 38o
#2 Finding Angle Measures • and are tangent to . Find the value of x. L M x° O 117° Since and are tangent to N and are right angles. LMNO is a quadrilateral whose angle measures have a sum of 360°.
Theorem 11-2 • If a line in the plane of a circle is perpendicular to a radius at its endpoint on the circle, then the line is tangent to the circle. A P B O
#3 Finding a Tangent • If NL = 4, LM = 7, and NM = 8, is tangent to a at L? M 8 7 4 L N
#4 Finding a Tangent • If NL = 7, LM = 24, and NM = 25, is tangent to a at L? N 25 7 M Yes L 24
Assignment • Page 586 • #1-3; 10-12