PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGANISMS
260 likes | 482 Vues
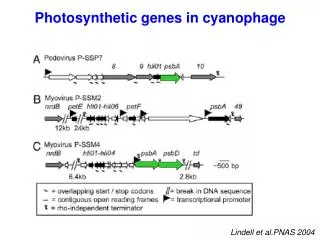
PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGANISMS. Section 3.1 Pages 138-145. Photosynthesis:. 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + light energy C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 carbon water glucose oxygen dioxide. Photosynthesizing organisms:. Plants Algae Some protists

PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGANISMS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGANISMS Section 3.1 Pages 138-145
Photosynthesis: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6 O2 carbon water glucose oxygen dioxide
Photosynthesizing organisms: • Plants • Algae • Some protists • Cyanobacteria All contain the pigment chlorophyll
Chlorophyll • Green pigment • Absorbs light energy • Several types: • chlorophyll a (blue-green) • chlorophyll b(yellow-green) Common forms
Chlorophyll: Molecular composition R • Porphyrin ring • Long hydrocarbon tail
Porphyrin ring • Mg atom, surrounded by a H.C. Ring • Delocalized e-s absorb energy • Hydrocarbon tail • Nonpolar • Anchors the molecule in membranes
Chlorophyll a vs. b R • a has a methyl group at R position • b contains an aldehyde (-COH) group Affects the type of light energy that can be absorbed
Cyanobacteria • aka “blue-green algae” • prokaryotic • unicellular • closely related to plant chloroplasts • photosynthesis & respiration are carried out on the cell membrane
Eukaryotic autotrophs • Contain chlorophyll within chloroplasts • Plants: • Leaves are the main sites of photosynthesis
Leaf structure • Minimizes distance gases need to travel to reach chloroplasts; and • maximizes surface area exposed to sunlight
Cross section of a leaf: Cuticle-Waxy. Protects the leaf from water loss.
Cross section of a leaf: Epidermis – Transparent layer that allows light to pass into the leaf
Cross section of a leaf: Mesophyll – Photosynthetic cells. Form the bulk of the plant leaf. Spongy, and Palisade types
Cross section of a leaf: Vascular bundles, aka veins Transport water/nutrients between parts of the plant
Stomata – Openings on the surface of a leaf • Open/close to regulate gas exchange between atmosphere & leaf Guardcells – Epidermal cells that surround stomata. • Regulate the size of the stomata stoma guard cell
Regulating stomata size Guard cells change shape in response to environmental conditions • Guard cells are turgid Stomata will open • Guard cells are flaccid Stomata will close In general, stomata are open during the day, and closed at night.
Shape/size of guard cell determined by osmosis in or out of cell. • Water flows in, guard cells swell • Direction of osmosis is determined by diffusion of K+ in/out of cell.
...but what determines direction of K+ diffusion?? • Sunlight activates proton pumps in the guard cell membrane • The pumps transport H+ out of the cells creates an electrochemical gradient • Gradient drives K+ into cells • Water follows by osmosis • Guard cells swell and stomata open
Transpiration Release of water vapour through the stomata of plants Assists photosynthesis by: • Pulling water, minerals, etc. up from the roots • Cooling the leaves down – prevents denaturation of enzymes
Double membrane • Interior is filled with the stroma • Membrane-bound thylakoid sacs within the stroma • stacked in columns (grana)
Photosynthesis occurs in the: • stroma, and • thylakoid membrane
Homework Pg. 145 #2-5