Holistic Optimization Techniques for Database Applications
10 likes | 130 Vues
This work presents a holistic approach to optimizing database applications through innovative techniques. By analyzing application programs and embedded queries, we employ program transformations such as equivalence rules and semantic-preserving reordering to enhance database interaction. Our DBridge tool, built on the Soot framework, enables efficient batch processing and asynchronous submissions of database queries. This results in significant performance improvements, enabling applications to perform other tasks during query execution and dramatically reducing execution time by up to 7x through effective batching and asynchronous strategies.

Holistic Optimization Techniques for Database Applications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
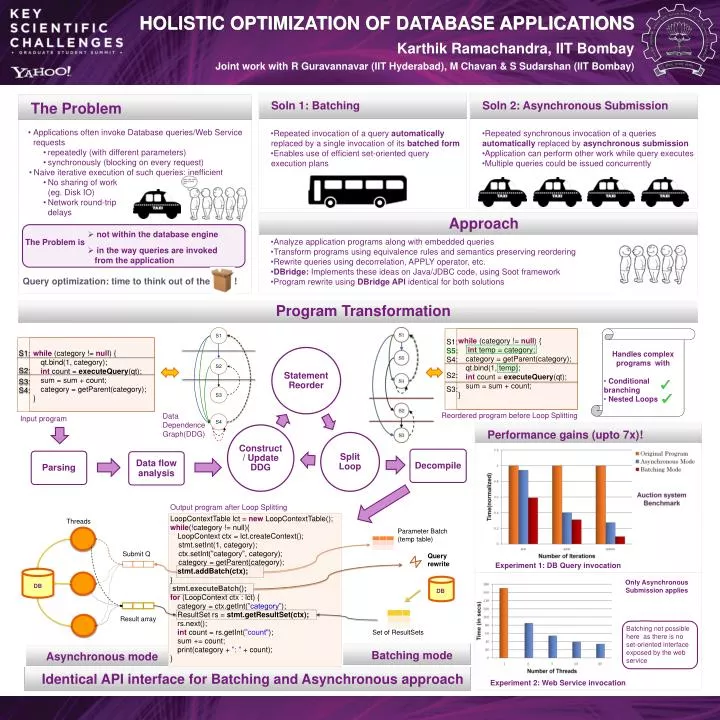
HOLISTIC OPTIMIZATION OF DATABASE APPLICATIONS KarthikRamachandra, IIT Bombay Joint work with R Guravannavar(IIT Hyderabad), M Chavan & S Sudarshan (IIT Bombay) LoopContextTable lct = new LoopContextTable(); while(!category != null){ LoopContext ctx = lct.createContext(); stmt.setInt(1, category); ctx.setInt(”category”, category); category = getParent(category); stmt.addBatch(ctx); } stmt.executeBatch(); for (LoopContext ctx : lct) { category = ctx.getInt(”category”); ResultSet rs = stmt.getResultSet(ctx); rs.next(); int count = rs.getInt(”count"); sum += count; print(category+ ”: ” +count); } S1 S2 S3 while(category!= null){ inttemp = category; category = getParent(category); qt.bind(1, temp); intcount = executeQuery(qt); sum = sum + count; } S1: S5: S4 S4: • Applications often invoke Database queries/Web Service requests • repeatedly (with different parameters) • synchronously (blocking on every request) • Naive iterative execution of such queries: inefficient • No sharing of work (eg. Disk IO) • Network round-trip delays The Problem S2: • Analyze application programs along with embedded queries • Transform programs using equivalence rules and semantics preserving reordering • Rewrite queries using decorrelation, APPLY operator, etc. • DBridge: Implements these ideas on Java/JDBC code, using Soot framework • Program rewrite using DBridge API identical for both solutions • Repeated invocation of a query automatically replaced by a single invocation of its batched form • Enables use of efficient set-oriented query execution plans • Repeated synchronous invocation of a queries automatically replaced by asynchronous submission • Application can perform other work while query executes • Multiple queries could be issued concurrently S3: Performance gains (upto 7x)! Soln 1: Batching Soln 2: Asynchronous Submission Approach Parsing Data flow analysis Decompile • not within the database engine The Problem is • in the way queries are invoked from the application S1: while(category!= null){ qt.bind(1, category); intcount = executeQuery(qt); sum = sum + count; category = getParent(category); } S2: Query optimization: time to think out of the box! S3: S4: Program Transformation • Handles complex programs with • Conditional branching • Nested Loops Threads Parameter Batch (temp table) Reordered program before Loop Splitting Data Dependence Graph(DDG) Input program DB Set of ResultSets Output program after Loop Splitting Submit Q Query rewrite Experiment 1: DB Query invocation Only Asynchronous Submission applies DB Result array Batching not possible here as there is no set-oriented interface exposed by the web service Batching mode Asynchronous mode Identical API interface for Batching and Asynchronous approach Experiment 2: Web Service invocation