ICS 101 Fall 2011 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
370 likes | 634 Vues
ICS 101 Fall 2011 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa. What is Artificial Intelligence ?. What is human intelligence ?. What are signs (activities, abilities etc) of human intelligence ?.

ICS 101 Fall 2011 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ICS 101 Fall 2011Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
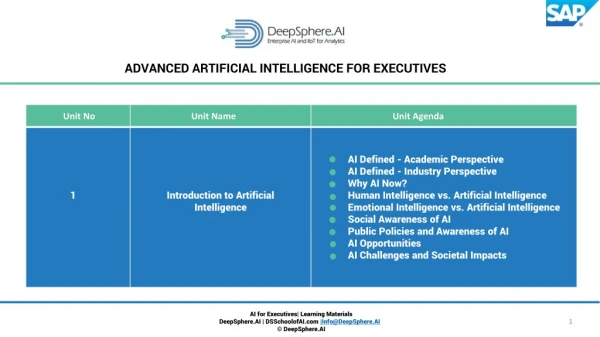
What is Artificial Intelligence ? Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
What is human intelligence ? Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
What are signs (activities, abilities etc) of human intelligence ? Exercise 1: Write down four examples in your worksheet Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Approaches to A.I. Human-oriented Rationalist Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Thinking Acting Humanly Acting Rationally Acting Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Definitions of AI (a) • “The exciting new effort to make computer think ... machines with minds, in the full and literal sense.” (Haugeland, 1985) • “[The automation of] activities that associate with human thinking, activities such as decision-making, problem solving, learning ...” (Bellman, 1978) • “The art of creating machines that perform functions that require intelligence when performed by people.” (Kurzweil, 1990) • “The study of how to make computers do things, at the moment, people are better.” (Rich and Knight, 1991) Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Definitions of AI (b) • “The study of mental faculties through the use of computational models.” (Charniak and McDermott, 1985) • “The study of the computations that make it possible to perceive, reason, and act.” (Winston, 1992) • “Computational Intelligence is the study of the design of intelligent agents.”(Poole et al., 1998) • “AI ... is concerned with intelligent behavior in artifacts.” (Nilsson, 1998) Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Acting Humanly: Turing Test (1950) Human • Operational test of intelligence • Anticipated all major arguments against AI in following 50 years • Suggested major components of AI: knowledge, reasoning, language understanding, learning ? A.I. Human Interrogator Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Thinking Humanly : Cognitive Science • AI thinks like humans do • How do humans think ? • How can we find out ? • Introspection • Psychological experiments • Brain imaging • The goal is to formulate computer programs that mimic how humans think and hence achieve AI! Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Thinking Rationally • Aristotle: what are correct arguments/thought processes? • Syllogism: • Socrates is a man; • All men are mortal • Therefore Socrates is mortal • Field of logic • AI programs represent knowledge using formal logic and solves problems using logical inference/reasoning. Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Acting Rationally • Acting rationally == doing the right thing • What is the “right thing” ? • Logical / rational • maximize goal achievement, given the available information • This approach is the focus of many AI efforts! • AI programs are rational agents : programs that act so as to achieve the best outcome or best expected outcome Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
AI Today • Robotic Vehicles: Google Self-Drive Car • Speech Recognition: Call routing, Call center • Autonomous planning: Mars Rover • Game Playing: Deep Blue, Watson • Spam Fighting • Logistic Planning: Dynamic Analysis & Replanning Tool (DART) • Robotics : Roomba • Machine Translation Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Intelligent Agents Agent Percepts • Perceives its environment through sensors • Acts upon the environment through actuators • Percepts – perceptual input at any given instant • Agent program implements how to map a sequence of percepts to an action Sensors Environment Agent Program Actuators Actions Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot A B • Vacuum Robot (“agent”) needs to keep two rooms A & B clean. It can sense which room it is in and whether the carpet in that room is dirty. It can either go Right, go Left, or Suck. ************ ************ Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot Agent Program Agent Percepts A B Sensors Environment Agent Program Actions Actuators ********* ********* Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Representation & Search • Newell & Simon argue that intelligent activity (human or machine) is achieved by: • Representing significant aspects of a problem using symbol patterns • Generating potential solutions by applying operations on the representation • Selecting a solution by searching among these possibilities Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Tic-Tac-Toe • 2 Player Game: Each gets a symbol 0 or X • Each player tries to get 3 of his/her symbol in a row/column/diagonal in a 3 by 3 grid. Player B Player A Player B Player A Player A Wins ! Player A Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: State Space for Tic-Tac-Toe ... ... ... ... ... ... Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Exercise A B • Draw the state space for the vacuum robot starting from the following initial state for the next two state transitions. ************ ************ Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Podcast Supplement Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Approaches to A.I. Human-oriented Rationalist Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Thinking Acting Humanly Acting Rationally Acting Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Acting Humanly: Turing Test (1950) Human • Operational test of intelligence • Anticipated all major arguments against AI in following 50 years • Suggested major components of AI: knowledge, reasoning, language understanding, learning ? A.I. Human Interrogator Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Thinking Humanly : Cognitive Science • AI thinks like humans do • How do humans think ? • How can we find out ? • Introspection • Psychological experiments • Brain imaging • The goal is to formulate computer programs that mimic how humans think and hence achieve AI! Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Thinking Rationally • Aristotle: what are correct arguments/thought processes? • Syllogism: • Socrates is a man; • All men are mortal • Therefore Socrates is mortal • Field of logic • AI programs represent knowledge using formal logic and solves problems using logical inference/reasoning. Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Acting Rationally • Acting rationally == doing the right thing • What is the “right thing” ? • Logical / rational • maximize goal achievement, given the available information • This approach is the focus of many AI efforts! AI programs are rational agents : programs that act so as to achieve the best outcome or best expected outcome Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Intelligent Agents Agent Sensors Percepts • Perceives its environment through sensors • Acts upon the environment through actuators • Percepts – perceptual input at any given instant • Agent program implements how to map a sequence of percepts to an action to achieve some goal Environment Agent Program Actuators Actions Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot (“Agent”) Agent Percepts A B • Goal/outcome: keep two rooms A & B clean. • Percepts: which room it is in and whether the carpet in that room is dirty. • Actions: go Right, go Left, or Suck. Sensors Environment Agent Program Actions Actuators ********* ********* Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot Agent Program Agent Percepts A B Sensors Environment Agent Program Actions Actuators ********* ********* Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Tic-Tac-Toe Agent Human Agent • Goal/outcome: Play by the rules and win • Percepts: the tic-tac-toe board and the human’s move on the board. • Actions: put a “0” on any of the empty cell on the board Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Car Driving Agent Agent Percepts • Goal/outcome: Navigate and drive to destination safely obeying traffic rules • Percepts: its own location, speed, direction, and location, speed, direction of nearby objects • Actions: accelerate, decelerate, hardstop, turn x degrees left, turn x degrees right, maintain speed Sensors Environment Agent Program Actions Actuators Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Representation & Search • Newell & Simon argue that intelligent activity (human or machine) is achieved by: • Representing significant aspects of a problem using symbol patterns • Generating potential solutions by applying operations on the representation • Selecting a solution by searching among these possibilities Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot A A A A B B B B • State representation: • Cleanliness status of each room • Location of robot • State Transitions (generating possibilities) • Triggered by actions of robot (L, R, S) • Goal states (selecting solutions) • Any state where both rooms are clean Right Suck Suck ***** ***** ***** ***** Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Vacuum Robot State Space R S A A A A A A A A B B B B B B B B L R S R R S R S L L R L L S ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** L R S ***** ***** L L R S Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: Tic-Tac-Toe • State representation: • Tic-tac-toe board • Location of X’s and 0’s • State Transitions (generating possibilities) • Triggered by players putting X/0 on empty cells • Goal states (selecting solutions) • Any state where symbols form a line Player A Player B Player A Player B Player A Player A Wins ! Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Example: State Space for Tic-Tac-Toe ... ... ... ... ... ... Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Summary • Four different approaches to AI • Acting vs Thinking • Human-oriented vs Rationalist • Intelligent Agents • Sensors • Actuators • Agent Program • Representation and Search • Representing the state of the problem • Generating the state space • Searching the state space for goal states Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa