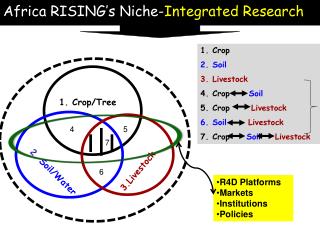
Agro-forestry & crop combination options
260 likes | 593 Vues
Agro-forestry & crop combination options. Dr Calliope Panoutsou Biomass Department CRES. Contents. Aim S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities & T hreats Biomass resources available in south EU Agro- biomass Forest biomass Current RTD projects Future options Future RTD needs

Agro-forestry & crop combination options
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Agro-forestry & crop combination options Dr Calliope Panoutsou Biomass Department CRES
Contents • Aim • Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats • Biomass resources available in south EU • Agro- biomass • Forest biomass • Current RTD projects • Future options • Future RTD needs • Challenges • Recommendations- Conclusions
Aim • Collecting information on experiences gained with and possibilities for dedicated bioenergy crop combinations as well as • agro-forestry options which promise to combine high yields with relatively low environmental impacts.
Strengths • Climate favors several resource options • Residual resources with low moisture • Energy crops with high yielding potential • Energy crops can be complementary to current activities in time and resources (human & machinery) • Uncertain policy framework (new CAP) leads farmers to seek new cropping options • Political pressure on RES & bioenergy (Biomass Action Plan) • Emissions & Biofuels Directives (2003/87/EC, 2003/30/EC) could be a means for high biomass demand
Weaknesses • Semi-arid conditions require irrigation • Landscape associated risks (erosion, water runoff, desertification levels) • Small farming size compared with central, northern EU member states • Lack of “fully” mechanized agriculture • RTD fragmented, reflecting great diversity of crops, supply routes and end uses. • Difficult forest management, fire risks, lack of road infrastructure, etc. • Need to evaluate the whole chain; an integrated approach to deliver quality, availability and cost targets and achieve competitiveness.
Opportunities • Identify dedicated low impact high yielding cropping systems suitable for med regions • Create supply chains combining residual forms and energy crops. • Establish fuel supply chains which will act as links among biomass producers & users • Evaluate resource options both for industrial & with waste fractions (e.g. energy properties (biorefinery supplies) • Combine agro- forestry biomass with waste streams (demolition wood, packaging paper, etc.) • Create communication channels & synergies with the farming & forestry community
Threats • Traditional “food” agriculture systems not aware of energy- industry markets • Variety of feedstocks with different physical- chemical properties • Lack of specified agricultural machinery for certain energy crops • Low knowledge levels in the farming & forestry communities • Complexity of issues & associated groups involved require prior to start- up planning and strong day-to-day coordination
Biomass energy in south EU • High growth rate in wind energy but slow expansion of biomass singled out as key reason for failure to reach targets. • Modest progress in southern countries. • Limited data for energy crops: RTD small scale fields cannot give answers for commercial scale up • Lack of forest management practices dedicated to energy in most south states
Growing stock(Million m3) EU N: 6,420 EU C: 10,546 EU S: 2,767 Annual increment, fellings (2000)
Current RTD projects • ENK6 CT2001 00524: Bioenergy chains for south Europe • Four perennial grasses: giant reed, cynara, switcgrass, miscanthus • Three thermochemical processes: combustion, gasification, pyrolysis • Whole chain economics & environmental assessments • Harvest window ensuring year round supply • Good time allocation of resources • Crops are complementary to current agricultural activities
Current RTD projects • Cynara cardunculus: BIOCARD 6FP • Perennial crop suitable to med conditions • Can be rainfed • Wide range of products from biodiesel, heat & electricity • Good potential for biorefinery feedstock…
Future RTD needs • Establish competitive supply chains to meet market requirements. • Optimise bioenergy systems, matching production options through to conversion requirements. • Improve know-how for stages between production and conversion.
Resource production Yield & Characteristics • Sustained high yields over long term under commercial (not research) conditions • Multi-cropping of selected perennial crops for energy • Optimise forest management systems also for energy • Agronomy to influence biomass quality • Combined approaches of residual biomass & energy crops examined at pre-commercial chains • Determine production systems that best integrate with chain including conversion requirements.
Harvesting & Collection Effectiveness & Speed • Test existing machinery • Develop and test new machines and components • Low contamination harvesting methods • Harvesting and collection must be effective and high speed, deliver feedstock in optimal state, and minimize site impacts
Storage & Transport Reliability & Quality • Minimization of risks: fire, health. • Ensure quality: feedstock physical specifications • Optimise technology for chips / bales / pellets • Assess different logistic structures, such as centralized fuel depots.
System integration • System sustainability – energy and emissions balance over life cycle of chain • System costs – vertical integration or each step as profit centre? • Stakeholders consultation – agro-industry, hauliers, energy industry, local communities. • Emergence of international trade of standardised biomass fuels – impacts? • Minimization of risk throughout the chain and demonstrating schemes can be financed.
Challenges • Supply the industry with secure raw material • Efficient land use by the use of whole- crop solutions as well as exploiting both fertile and marginal land. • Ensure that both primary production and residues will be evaluated for their energy potential • Sustainability in biomass production- handling • Improve the acceptability of biomass filiere by strengthening the communication channels among the relevant stakeholders, especially the farming- forestry sectors with the respective fuel and energy sectors. • Local biomass production & international biomass trade
Future options • Perennial crops, like cynara, giant reed, miscanthus and SRC like eycalypts, robinia • Annual crops possibilities for double cropping like in Germany • Green crop harvesting for AD-biogas and a second crop option for bioenergy – biofuels?? • Integrate energy crops within the current crop patterns as complementary activities • Ensure harvest window with crop selection • Integrate forest & agricultural activities to ensure supply
Recommendations • Integrated waste management strategies • Introduce efficient land use strategies, complementary to current systems and regional characteristics • Sustainable forest residual harvest for energy prevents fire risks. “Make sure the message is clear enough!!”
Conclusions- Next Steps To be completed with your valuable input!! Thank you for your attention