Integrating CCRS with Social Studies: Strategies and Standards for Educators
460 likes | 580 Vues
This comprehensive guide, prepared by David A. Johnson of the Northern Michigan Learning Consortium, explores the integration of the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) within Social Studies education. Attendees will learn how CCRS can be applied in their classrooms and how to creatively engage students using historical contexts. The session aims to clarify the relationship between CCRS and literacy in the Social Studies classroom, provide practical classroom strategies, and encourage collaborative planning among educators.

Integrating CCRS with Social Studies: Strategies and Standards for Educators
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Social Studies and the CCRS David. A Johnson Social Studies Consultant Northern Michigan Learning Consortium David.johnson@wmisd.org Prepared November 2011
Introductions • Northern Michigan Learning Consortium • E-Mail Lists • Upcoming training dates • Time Machine
Time Machine • Take a minute to think…if you could go back to any historical time period, where would you go? • Why would you want to go there? • Would you want to be born there or just visit? • Would you want to stay? • Why?
Time Machine Wrap Up • Writing Standard 1 asks us to: • Write and support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence by: • Organizing the reasons and evidence clearly • Supporting claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence using credible sources and demonstrating an understanding of the topic or text • Use words, phrases, and clauses to clarify the relationships among claims and reasons • Establish and maintain a formal style • Provide a concluding statement that follows the argument presented. We didn’t hit all the points here, but…how could we have changed it to meet the evidence and conclusion piece?
Goals and Objectives for today: • You will be able to • …describe how the Career and College Readiness Standards apply to Social Studies • …identify how several of the Core Standards could be used in your own classrooms starting tomorrow • …understand how the literacy piece fits into the Social Studies classroom • Rate your knowledge coming in today…
What Is The Common Core? • New literacy standards adopted by Michigan and many other states. • Based around College and Career Readiness Standards. • Replace GLCE/HSCE in English/Language Arts and Math • Add to GLCE/HSCE in all other subjects.
What Is The Common Core? • End of grade expectations • Same 10 anchor standards at every grade level. • Varying degrees of complexity depending on which level
What Is The Common Core? • “Students advancing through the grades are expected to meet each year’s grade-specific standards, retain or further develop skills and understandings mastered in preceding grades, and work steadily toward meeting the more general expectations described by the CCR standards.” • Grade level in Kindergarten-5th grade • Grade Spans for 6-8, 9-10, 11-12
What Is The Common Core? • Texts and programs not prescribed/spelled out • Teacher is free to bring materials into their curriculum as they see fit. • Key comes in Text Complexity
All K-5 Teachers • 10 Reading Standards – Narrative Text • 10 Reading Standards – Informational Text • 10 Writing Standards • 6 Speaking and Listening Standards • 6 Whole Language
What About The Other Subjects? http://www.youtube.com/user/TheHuntInstitute#p/c/9F9C431FF82A15B5/5/1zHWMfg_8r0
Science, Social Studies, and other Subjects 6-12 • The Standards insist that instruction in reading, writing, speaking, listening, and language be a shared responsibility within the school • 10 Reading Standards (6-8), (9-10), (11-12) • 10 Writing Standards (6-8), (9-10), (11-12)
The 6 Shifts • Increase in Non-Fiction texts • Content Area Literacy • Increased Text Complexity • Focus on Text Based Questioning • Argumentative Writing • Academic Vocabulary
What The Standards Aren’t • 1.The Standards define what all students are expected to know and be able to do, not how teachers should teach • 2. While the Standards focus on what is most essential, they do not describe all that can or should be taught • 3. The Standards do not define the nature of advanced work for students who meet the Standards prior to the end of high school.
What The Standards Aren’t • 4. The Standards set grade-specific standards but do not define the intervention methods or materials necessary to support students who are well below or well above grade-level expectations.
Resources to Help • MC3 • NMLC Wiki
6 Shifts Activity • Number off 1-6 • Each group is going to be given a “shift” • In groups, you will work collaboratively to build a list of ways Social Studies can help meet this new requirement. • Lists will be compiled together and sent out to all participants
6 Shifts Activity Wrap Up • Writing Standard 7 asks us to: • Conduct short research projects to answera question, drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions for further research and investigation. • How well did we hit this one? What could we tweak?
Pre-Break check in… • Questions? • Door Prizes
Break! • Be back in 15 minutes!
GLCE/HSCE vs CCRS • The standards do not replace your GLCE/HSCE in Social Studies. • They can help focus activities that relate to GLCE/HSCE you’re already teaching
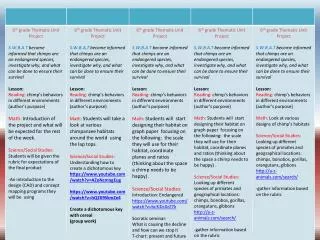
Writing 1 K: Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose opinion pieces in which they tell a reader the topic or the name of the book they are writing about and state an opinion or preference about the topic or book (e.g., My favorite book is . . .). 1: Write opinion pieces in which they introduce the topic or name the book they are writing about, state an opinion, supply a reason for the opinion, and provide some sense of closure. 2: Write opinion pieces in which they introduce the topic or book they are writing about, state an opinion, supply reasons that support the opinion, use linking words (e.g., because, and, also) to connect opinion and reasons, and provide a concluding statement or section.
Writing 2 K: Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose informative/explanatory texts in which they name what they are writing about and supply some information about the topic. 1: Write informative/explanatory texts in which they name a topic, supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure. 2: Write informative/explanatory texts in which they introduce a topic, use facts and definitions to develop points, and provide a concluding statement or section.
Writing 3 K: Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to narrate a single event or several loosely linked events, tell about the events in the order in which they occurred, and provide a reaction to what happened. 1:Write narratives in which they recount two or more appropriately sequenced events, include some details regarding what happened, use temporal words to signal event order, and provide some sense of closure. 2: Write narratives in which they recount a well-elaborated event or short sequence of events, include details to describe actions, thoughts, and feelings, use temporal words to signal event order, and provide a sense of closure.
Content Writing 3 Not applicable as a separate requirement (6-12)
Writing 4 K-2: Begins in 3rd Grade 3: With guidance and support from adults, produce writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task and purpose. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in standards 1–3 above.) 4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in standards 1–3 above.) 5: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in standards 1–3 above.) 6-8: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. 9-10: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. 11-12: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.
K: With guidance and support from adults, respond to questions and suggestions from peers and add details to strengthen writing as needed. 1: With guidance and support from adults, focus on a topic, respond to questions and suggestions from peers, and add details to strengthen writing as needed. 2: With guidance and support from adults and peers, focus on a topic and strengthen writing as needed by revising and editing. 3: With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing. 4: With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing. 5: With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach. 6-8: With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. 9-10: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. 11-12: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. Writing 5
Writing 6 K: With guidance and support from adults, explore a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in collaboration with peers. 1: With guidance and support from adults, use a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in collaboration with peers. 2: With guidance and support from adults, use a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in collaboration with peers. 3: With guidance and support from adults, use technology to produce and publish writing (using keyboarding skills) as well as to interact and collaborate with others. 4: With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others; demonstrate sufficient command of keyboarding skills to type a minimum of one page in a single sitting. 5: With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others; demonstrate sufficient command of keyboarding skills to type a minimum of two pages in a single sitting. 6-8: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and present the relationships between information and ideas clearly and efficiently. 9-10: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. 11-12: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information.
Writing 7 K: Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., explore a number of books by a favorite author and express opinions about them). 1: Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., explore a number of “how-to” books on a given topic and use them to write a sequence of instructions). 2: Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., read a number of books on a single topic to produce a report; record science observations). 3: Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. 4: Conduct short research projects that build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic. 5: Conduct short research projects that use several sources to build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic. 6-8: Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration. 9-10: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. 11-12: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation
Writing 8 K: With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question 1: With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. 2: Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question 3: Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. 4: Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; take notes and categorize information, and provide a list of sources. 5: Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; summarize or paraphrase information in notes and finished work, and provide a list of sources. 6-8: Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. 9-10: Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. 11-12: Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the strengths and limitations of each source in terms of the specific task, purpose, and audience; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and overreliance on any one source and following a standard format for citation.
Writing 9 K: Begins in 4th grade 1: Begins in 4th grade 2: Begins in 4th grade 3: Begins in 4th grade
Content Writing 9 6-8: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis reflection, and research. 9-10: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. 11-12: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Writing 10 K-2: Begins in 3rd Grade 3: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 4: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 5: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 6-8: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 9-10: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 11-12: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.
References National Governors Association, (2010). English/language arts standards Retrieved from http://www.corestandards.org Michigan Department of Education, (2010). K-12 ela crosswalk Retrieved from http://www.michigan.gov/mde/0,4615,7-140--232021--,00.html Michigan Department of Education, (2010). 6-12 content literacy crosswalk Retrieved from Michigan Department of Education, (2010). K-12 ela crosswalk Retrieved from http://www.michigan.gov/mde/0,4615,7-140--232021--,00.html
Post Lecture Check In • Questions? • Door Prizes
Activity • Break into grade level (or grade span) teams • Take the provided copy of your GLCE and your CCRS brochures • What are the EASIEST reading and writing standards to apply to your content area • What are the tough ones? • Brainstorm some ways your current content expectations could be used to meet the easy and hard ones in your grade level/span teams
Activity Wrap Up • Reading Standard 2 asks you to determine the central ideas or information in primary or secondary sources; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. • Writing Standard 8 asks you to: gather relevant information from multiple sources, assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation.
Final Pre-Lunch Activity • Take one resource and in your groups: • Create a brief narrative describing how this resource could be used to hit 1-2 CCRS reading standards, 1-2 CCRS Writing Standards (Approximately one short paragraph for each standard) • Don’t forget the WHY!
Grouping Activity Wrap Up • Writing Standard 4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. • Writing Standard 10: Write routinely over extended time frames and shorter time frames for a range of discipline specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Goals and Objectives for today: • You will be able to • …describe how the Career and College Readiness Standards apply to Social Studies • …identify how several of the Core Standards could be used in your own classrooms starting tomorrow • …understand how the literacy piece fits into the Social Studies classroom • Rate Your Experience Thus-Far
Pre-Lunch Questions? • Door Prizes • Be Back in 1 hour!
Welcome Back! • Afternoon Focus: The Literacy Piece • Rebecca Shankland
Post Activity Check In… • Questions? • Door Prizes
Wrap Up • Resource Sheets • Evaluations • My contact Info • Final Thoughts…