Exploring Pedigrees and Punnett Squares in Genetics
160 likes | 267 Vues
This lesson focuses on understanding genetic inheritance patterns through pedigree analysis and Punnett squares. Students will engage in filling out Punnett squares to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses, specifically examining traits like dominant red hair and homozygous yellow hair. Activities include investigating characteristics of created creatures, discussing true statements about reproduction across organisms, and identifying genetic representations of traits. The objective is to deepen students' grasp of heredity concepts and prepare them for future assessments.

Exploring Pedigrees and Punnett Squares in Genetics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
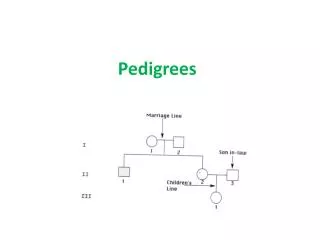
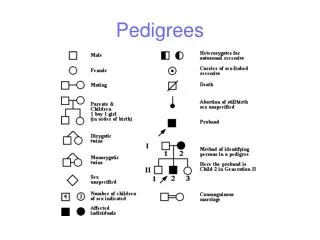
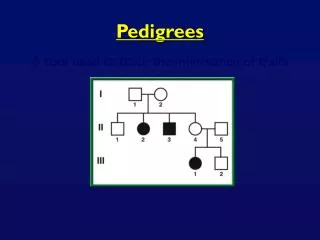
Patterns in Pedigrees 2-15-11
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: Heterozygous dominant red hair Homozygous yellow hair R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
2-15-11 Bell Work: Fill in the Punnett Square: R r r r
Daily Review: Yesterday we worked on our creatures. What is one characteristic of your creature that you like?
2-15-11 Objective: I will investigate pedigrees. HW: None
Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. only single-celled organisms can reproduce sexually B. only single-celled organisms can reproduce asexually C. only multi-cellular organisms can reproduce asexually D. none of the above
Task: Read pages D-64 to D-71.
Closure: On page D-71, which parents are heterozygous for type O blood?
Long Term Memory Review • Assume that a genetic trait is represented by the letter “a.” Which of the following would most likely be used to represent the recessive condition? • AA • Aa • aa • none of the above