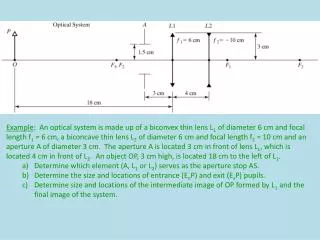
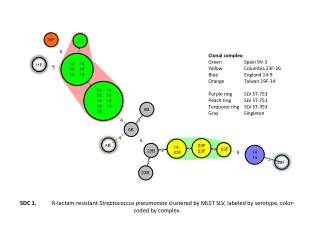
14 Common Misconceptions About bts light stick
This really is just A fast assessment of the military Bomb by BTS Mild Adhere. When you are a web based Military Bomb or Military.com participant, you understand all concerning this program. This can be the most recent Model in the BTS Military Bomb series. The most crucial objective of the new series is to maintain up with The latest news, BTS Mild Adhere is the primary one particular to take action. This system includes almost everything you could possibly need to know concerning the BTS Army Bomb. Together with the new edition you might have a chance to invest in upgrades at at any time for just one minimal price tag. Additionally, it comes along with a member's forum where by members can talk with regards to their encounters. As with all other BTS products and solutions, the military Bomb Mild Adhere is full of features. The text box is incredible and you will alter the text to whichever you would like. The graphics and track record are vibrant and entertaining and it's been developed so you're able to transfer it any where on your monitor. Also you can use the flash plug-in so as to add photos to your text bins. The program was made for gamers who prefer to play around the fly and don't have lots of the perfect time to exercise. The better part with regards to the new edition of the military Bomb Light-weight Stick is which you could play the game versus the pc. Which means You may use the program in your spare time and get paid more money also. It's also possible to find out if you will get the ideal moments away from the opposite gamers and keep at the top of the chief board. The original Model on the BTS Military Bomb employs the old kind of touch screen engineering as well as the graphics had been really limited. The sport was really simplistic and didn't allow you to make use of your creativeness. The new version has all the things you can want including the correct side buttons, and also the pop up flash screens. The graphics are very good and the graphics in the Army Bomb Light-weight Adhere have not been better. The program is full of awesome characteristics for example flash graphics and a pleasant programming interface to generate your participating in encounter a lot more enjoyable. The BTS Army Bomb Mild Stick is the main plan that includes flash graphics and people are present in the packages on each of the other versions of the program. The display measurement is probably the most important benefits of the new version of the military Bomb Gentle Stick method. The new software means that you can move it on the decrease right within your display for a lot less vertical House than right before. Overall the BTS Military Bomb Light-weight Stick is a fantastic method and When you have been a BTS player up to now, you can find that the newer Variation is even better. Even When you've got not been a participant, you ought to be pretty pleased with The brand new method since it has lots of new options that you will like.
32 views • 1 slides