Blood In Your Body
110 likes | 288 Vues
Blood In Your Body . By: A riana H ernandez 3/20/12 Grade 7 th B204 . introduction. http:// science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/life/human-biology/blood.htm

Blood In Your Body
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Blood In Your Body By: Ariana Hernandez 3/20/12 Grade 7th B204 Ariana Hernandez
introduction • http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/life/human-biology/blood.htm • Unless you need to have blood drawn, donate it or have to stop its flow after an injury, you probably don't think much about it. But blood is the most commonly tested part of the body, and it is truly the river of life. • The adult human body contains approximately 5 liters (5.3 quarts) of blood; it makes up 7 to 8 percent of a person's body weight. Approximately 2.75 to 3 liters of blood is plasma and the rest is the cellular portion. • This life-giving product carries oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, and carries carbon dioxide and other waste products back to the lungs, kidneys and liver for disposal. It fights against infection and helps heal wounds, so we can stay healthy. Ariana Hernandez
blood typing • http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/landsteiner/readmore.html • There are 2 types of blood like red cells can crack and cause toxic reactions. • An adult human has about 4–6 liters of blood circulating in the body. Among other things, blood transports oxygen to various parts of the body. Ariana Hernandez
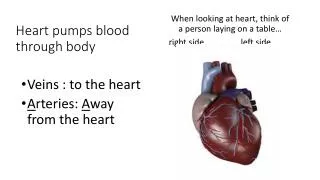
heart • You need to be careful with your heart because if you poke your heart you going to be dead because you are losing all lot of blood. • If someone shoots you if someone see you that the other person did that to you tell the person that has a telephone to call the police and the Ambulance to come for you because you are losing blood and the Ambulace take you to a hospital. Ariana Hernandez
Blood in your body • http://ask.yahoo.com/20000612.html • Both sites claim that the human body contains approximately 6 quarts (or 5.6 liters) of blood. The PBS site goes on to offer several other interesting tidbits: • In one day, your blood travels nearly 12,000 miles. • Your heart beats around 35 million times per year. • Your heart pumps a million barrels of blood during the average lifetime -- enough to fill three supertankers Ariana Hernandez
blood of kids or human • http://kidshealth.org/parent/general/body_basics/blood.html • Humans can't live without blood. Without blood, the body's organs couldn't get the oxygen and nutrients they need to survive, we couldn't keep warm or cool off, fight infections, or get rid of our own waste products. Without enough blood, we'd weaken and die. • Here are the basics about the mysterious, life-sustaining fluid called blood. • Arteries carry oxygenated blood (blood that has received oxygen from the lungs) from the heart to the rest of the body. • Blood then travels through veins back to the heart and lungs, where it receives more oxygen • There 3 blood there called • red blood cells (RBCs) • white blood cells (WBCs) • platelets Ariana Hernandez
the human heart • http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/blood.html • The average adult has about five liters of blood living inside of their body, coursing through their vessels, delivering essential elements, and removing harmful wastes. Without blood, the human body would stop working. • Blood is the fluid of life, transporting oxygen from the lungs to body tissue and carbon dioxide from body tissue to the lungs. Blood is the fluid of growth, transporting nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughout the body. Blood is the fluid of health, transporting disease fighting substances to the tissue and waste to the kidneys. Ariana Hernandez
white blood • http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/white.html • Whenever a germ or infection. Whenever a germ or infection enters the body, the white blood cells snap to attention and race toward the scene of the crime. The white blood cells are continually on the lookout for signs of disease. When a germ does appear, the white blood cells have a variety of ways by which they can attack. Some will produce protective antibodies that will overpower the germ. Others will surround and devour the bacteria. Ariana Hernandez
red blood • http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/red.html • Red blood cells perform the most important blood duty. A single drop of blood contains millions of red blood cells which are constantly traveling through your body delivering oxygen and removing waste. If they weren't, your body would slowly die. • Over time, the red blood cells get worn out and eventually die. The average life cycle of a red blood cell is 120 days. Your bones are continually producing new blood cells, replenishing your supply. The blood itself, however, is re-circulated throughout your body, not being remade all of the time. • Since the human body is continually making more blood, it is safe for healthy adults to donate blood. The blood is then stored for use in emergency situations. Initially after giving blood, the donor may feel some momentary light-headedness due to the loss of oxygen-rich red blood cells and blood sugar. The body quickly stabilizes itself. Ariana Hernandez
Blood Pressure • http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hbp/ • Blood pressure is measured as systolic (sis-TOL-ik) and diastolic (di-a-STOL-ik) pressures. "Systolic" refers to blood pressure when the heart beats while pumping blood. "Diastolic" refers to blood pressure when the heart is at rest between beats. • You most often will see blood pressure numbers written with the systolic number above or before the diastolic number, such as 120/80 mmHg. (The mmHg is millimeters of mercury—the units used to measure blood pressure.) • The table below shows normal blood pressure numbers for adults. It also shows which numbers put you at greater risk for health problems. Ariana Hernandez
Blood in urine • http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/blood-in-urine/DS01013/DSECTION=causes • Urinary tract infections may occur when bacteria enter your body through the urethra and begin to multiply in your bladder. Symptoms can include a persistent urge to urinate, pain and burning with urination, and extremely strong-smelling urine. For some people, especially older adults, the only sign of illness may be microscopic blood. • The minerals in concentrated urine sometimes precipitate out, forming crystals on the walls of your kidneys or bladder. Over time, the crystals can become small, hard stones. The stones are generally painless, and you probably won't know you have them unless they cause a blockage or are being passed. Then, there's usually no mistaking the symptoms — kidney stones, especially, can cause excruciating pain. Bladder or kidney stones can also cause both gross and microscopic bleeding. • Visible urinary bleeding may be a sign of advanced kidney, bladder or prostate cancer. Unfortunately, you may not have signs or symptoms in the early stages, when these cancers are more treatable. Ariana Hernandez