The Immune System
330 likes | 553 Vues
The Immune System. Disease Transmission. Robert Koch- “father of disease” research focused on anthrax Koch’s Postulates. NonSpecific Defenses. Initial reaction of body to ALL pathogens Pathogen -any agent that causes disease Ex: bacteria, virus, fungi, parasites

The Immune System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Disease Transmission • Robert Koch- “father of disease” • research focused on anthrax • Koch’s Postulates
NonSpecific Defenses • Initial reaction of body to ALL pathogens • Pathogen-any agent that causes disease • Ex: bacteria, virus, fungi, parasites • Come into contact with the body by: • Air • Food • Water • Person-to-person contact • Animal bites
NonSpecificDefenses:First Line of Defense • Skin – prevents entry • Oil – traps and kills invaders • Sweat-have toxins that can kill bacteria • Mucous Membranes – epithelial tissue that protect the interior surfaces of the body. • Mucous-sticky fluid that traps pathogens • Hair/Cilia • Respiratory tract into digestive tract • Tears • Saliva • Ear wax
NonSpecific Defenses:Second Line of Defense If a pathogen penetrates the first line of defense... Inflammatory Response: series of reactions that suppress infection and speed up recovery. • Cells are damaged. Ex: cut, pathogen invasion • Damaged cells release histamine • Causes increased blood flow and permeability of blood vessels around injured area • Histamine causes redness, swelling, warmth, pain • Sends signal to white blood cells to come • White blood cells (Phagocytes) arrive • Phagocytes ingest and destroy pathogens • 2 Types of Phagocytes: Neutrophils & Macrophages • Platelets arrive-seal off surrounding tissues and stop pathogens from entering the rest of the body
NonSpecific Defenses:Second Line of Defense • Natural Killer Cells-large white blood cells that attack pathogen-infected cells • Can kill cancer cells and virus-infected cells • Pierces cell membrane to kill the cell • Fever • Increase in body temperature • Slows growth of bacteria and viruses • Promotes WBC activity • Complement System • Proteins circulate in blood and become active when they encounter certain pathogens • Some puncture infected cell membranes to kill the cell • Interferon • Protein released by virus-infected cells • Causes nearby cells to make proteins that help them resist the virus infection
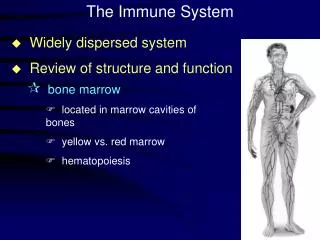
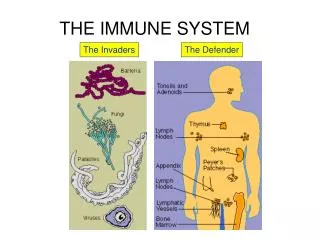
Specific DefensesThe Immune System When pathogens get past the NonSpecific Defense… Aimed at SPECIFIC pathogens • Immune System-cells and tissues that recognize and attack foreign substances • Tissues: • Bone marrow-makes lymphocytes • Thymus-gland where T cells mature • Lymph nodes-contain lymphocytes, filter lymph • Spleen-stores healthy blood cells, breaks down old blood cells, helps develop lymphocytes and other WBC, collects pathogens • Tonsils & Adenoids- masses of lymph tissue found in nose and throat that contain lymphocytes which produce antibodies • Cells: • Lymphocytes (WBC of the immune system) • 2 Types: • B Cells-made in bone marrow and mature there • T Cells-made in bone marrow, but mature in thymus
Recognizing Pathogens • Lymphocytes react to presence of antigens • Antigens-proteins on the surface of pathogens • Lymphocytes have unique receptors on surface that match specific antigens • Matching lymphocytes bind to antigen to start attack • Immune Response-reaction of the body against pathogens
Immune Response • An immune response begins with: • 1) Macrophage engulfs a pathogen • 2) Macrophage displays fragments of the pathogen’s antigens on its surface • 3) Helper T cell (lymphocyte) with matching receptors to the antigens binds to the macrophage • 4) Macrophage releases proteins that activate more helper T cells
Immune Response-Part 1 • The immune response occurs in 2 parts, which happen simultaneously • Part 1- Cell-Mediated Immune Response • Increase in Helper T cells and their division rates • Cytotoxic T cells are produced • Recognize and destroy pathogen-infected cells • Cytotoxic T cells have receptors that match antigens • Puncture the cell membrane to kill it
Immune Response-Part 2 • Part 2- HumoralImmune Response • B cells that have matching receptors to the antigen divide • Change into plasma cells and memory cells • Plasma cells-make antibodies • Antibodies-defensive proteins that are released into blood • Antibodies bind to specific antigen • They do not destroy the pathogens directly
Primary and Secondary Immune Responses • Some B cells turn into memory cells • Lymphocytes that will not respond the 1st time they meet an antigen, but will recognize and attack with later infections • Explains why you get most diseases only once • Primary Immune Response • First time the body encounters an antigen • Memory cells produced for that specific antigen • Secondary Immune Response • Later infection by the same pathogen • Memory cells respond faster and stronger • Exception: Cold and Flu viruses
Immunity and Vaccinations • Immunity-the ability to resist an infectious disease • Memory cells • Vaccinations • Vaccine-solution that contains a dead or weakened pathogen • Body produces primary immune response • Memory cells • Booster shots
Immune System Problems • Can react to harmless antigens in ways that can be harmful • Allergies, Asthma, Autoimmune Diseases • Allergy-a physical response to an antigen • Many symptoms due to histamine • Antihistamines-drugs that counteract effects of histamines and relieve symptoms of allergies
Immune System Problems • Allergies can trigger Asthma • Respiratory disorder • Bronchioles narrow • Swelling and inflammation • Difficulty breathing • Autoimmune Diseases • Disease where the immune system attacks the organism’s own cells • Ex: Multiple sclerosis • Nervous system • T cells attack insulating material in nerve cells in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves in eye • Cause weakness, tingling, blurred vision • Severe cases can cause paralysis, blindness, death
HIV and AIDS • AIDS- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome • The immune system loses its ability to fight off pathogens and cancers • AIDS results from infection by HIV • HIV-Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Destroys Helper T cellscripples the immune systemleads to AIDS • Opportunistic Infections-illnesses caused by pathogens that produce disease in people with weakened immune systems • Usually these pathogens don’t create problems in healthy people • HIV does NOT cause death, but AIDS is fatal • Death caused by weakened immune system’s inability to fight opportunistic infections and cancers • HIV is transmitted by body fluids and contaminated needles *PLAY DISCOVERYEDUCATION VIDEO*