Types of Systems
560 likes | 984 Vues
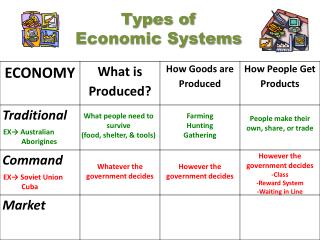
Types of Systems. Closed system and Open System. Closed system. Self contained. MATTER stays in. Energy moves freely in and out Example:. Open System. Matter and energy move in and out freely More complicated Very common in nature Example: river. Open or closed system?.

Types of Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Types of Systems Closed system and Open System
Closed system • Self contained. MATTER stays in. • Energy moves freely in and out • Example:
Open System • Matterandenergy move in and out freely • More complicated • Very common in nature • Example: river
Types of Spheres • Hydrosphere • Atmosphere • Geosphere • Biosphere
Hydrosphere • All the liquid • Lakes, rivers • Oceans • Glaciers • Aquifers
Of the hydrosphere…. • Oceans (salt water) 97.5% • Fresh water (drinkable) 2.5% • Frozen /ice (glaciers) (¾) • Ground water (aquifers) • Rivers / lakes • Atmosphere
Atmosphere • Gaseous envelope around earth • Half of it below 3.5 miles (5.6 meters) • 90% occurs within 10 miles (16 km) of the surface Purpose • Light (Radiation) protection • Energy exchange • Breathing
Solid Earth • Also known as Geosphere • Parts • Core • Dense center -Mantle • Less dense solid/liquid • Crust • Thin outer crust
Biosphere • All living things on the planet. • The other 3 spheres made biosphere possible! • Examples: • everything from single-cell protozoa to giant redwoods to humans. • Humans are changing the other 3 spheres!
Earth • Ocean basins and continents • Continents • Ave. elevation 2750 feet above sea level (840 m) • Ocean • Ave. depth 12500 feet (3800 m) Continents stand nearly 3 miles above the sea floor (4640 m)
Earth System • Closed or Open?
Select one picture describe how all four of earth’s spheres interact.
Cycles • A sequence of repeating events • Duration varies • Slow: repeat over a long period • of time – millions of years • Fast: repeat in a short amount of time
Types of Cycles • Water • Carbon • Energy
Hydrologic Cycle • The continuous circulation of water • Water in all three phases • Solid ice, liquid water, gaseous water vapor.
Water enters the atmosphere by evaporation (from oceans and lakes) and • transpiration (from plants) also called - evapotranspiration. • Water leaves the atmosphere as precipitation from clouds in the form of rain, snow.
Carbon Cycle • Carbon (C) • Biogeochemical cycle • “building block of life” • Many forms: solid coal and diamond, liquid oil, gaseous methane and carbon dioxide CO2 • Parts take various amounts of time
Energy Cycle • Movement of energy • Sources • Sun • Geothermal • Tidal • 40% of energy from sun reflected back
Source: Sun • Solar • 99.985%
Geothermal • Heat from within the Earth • 0.013%
Tidal Energy • Moon pulls on the Earth’s oceans creating tides • 0.002%
Laws of Thermodynamics • 1st law • Energy can not be created nor destroyed • Energy can only change forms • 2nd Law • When energy changes it becomes less concentrated and less useful, i.e. car engine loses heat as it runs
Effect of earth on Energy • Albedo • Percentage of Sun’s energy that is reflected back intospace without being changed (used) • Snow 80-90% • Desert 40-50% • Forest 5-10% • Earth overall 30% • Albedo can change (seasons)
Human activity and the cycles • Any human activity changes the cycles, both positively and negatively.